Hercules Metals Intersects 480 Meters of 0.47% Cu, 82 ppm Mo, including 55 Meters of 1.5% Cu

Hercules Metals Corp. (TSX-V: BIG) (OTCQB: BADEF) (FSE: C0X) is pleased to announce multiple broad copper intercepts from its Phase III drilling program on the newly discovered Leviathan porphyry copper system in western Idaho.
Highlights
- 140-meter step-out delivers similar hypogene enrichment to discovery hole HER-23-05, including 55 m of 1.5% Cu, within a broader intercept of 480 meters of 0.47% Cu, 82 ppm Mo, representing the longest intercept reported to date.
- Additional step-out holes planned to test its potential northeast-southwest trend extending towards HER-24-12, as well as down-plunge to the southeast (Fig. 1).
- Large step-out drilling outlines a 1.6 km x 1.1 km oval-shaped enrichment blanket which remains open.
- Drilling continues to vector toward the potassic core of the system and test for additional centers to the east within a large untested soil anomaly.
- Legacy Drilling has successfully completed the first RC hole to significant depth in challenging ground, demonstrating the potential to increase drilling production and lower the overall costs.
- Drilling progresses with two diamond core rigs and one RC rig and remains financed through to the end of 2025.
Chris Paul, CEO and Director of the Company, noted: “We are pleased with the grade and continuity returned over broad intervals in the system. The phyllic cap and hypogene enrichment blanket have expanded now to 1.6 km x 1.1 km, leading to new interpretations of the potential geometry and scale of the system. We’ve been able to work through drilling challenges faced at the start of the season and are now seeing strong production with the addition of Legacy’s RC rig. As production increases, it continues to generate new targets and vector us toward the core of the system.
As drilling moves into new target areas, we’re able to further test extensions of the widespread hypogene enrichment blanket. Hypogene enrichment is a rare phenomenon that only occurs in a small number of systems globally, but can often significantly upgrade the overall metal endowment. It remains to be seen if it extends into an as yet undiscovered high-grade potassic core.”
Table 1: Significant Intercepts1
| Hole ID | From (m) | To (m) | Interval (m) | Cu (%) | Ag (g/t) | Mo (ppm) |
| HER-24-01 | 256.37 | 411.24 | 154.87 | 0.44 | 10.87 | 64 |
| including | 256.37 | 339.85 | 83.48 | 0.67 | 18.88 | 67 |
| including | 256.37 | 286.51 | 30.14 | 1.11 | 48.48 | 32 |
| HER-24-02 | 297.91 | 327.66 | 29.75 | 0.18 | 0.46 | 14 |
| HER-24-03 | 207.9 | 224.52 | 16.62 | 0.47 | 0.67 | 6 |
| HER-24-04 | 266.49 | 484.33 | 217.84 | 0.33 | 2.10 | 59 |
| including | 266.49 | 323.55 | 57.06 | 0.55 | 2.68 | 64 |
| HER-24-06 | 471.53 | 509.32 | 37.79 | 0.53 | 17.9 | 97 |
| AND | 588.26 | 637.58 | 49.32 | 0.46 | 3.26 | 93 |
| HER-24-08 | 242.32 | 721.77 | 479.55 | 0.47 | 0.67 | 82 |
| including | 242.32 | 388.62 | 146.3 | 0.84 | 0.77 | 61 |
| including | 242.32 | 296.88 | 54.56 | 1.47 | 0.95 | 39 |
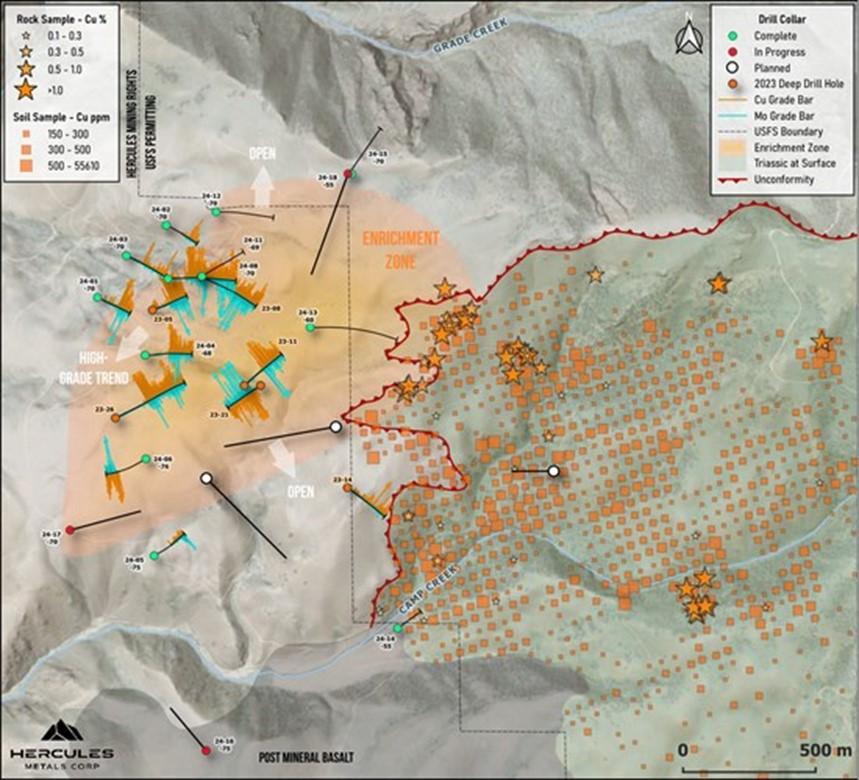
Figure 1: Drill Plan with grade bars for copper (orange) and molybdenum (blue) for holes with assays received. Approximate surface projection of enrichment blanket shown in orange. System remains open. Potential planned holes shown in white collars.
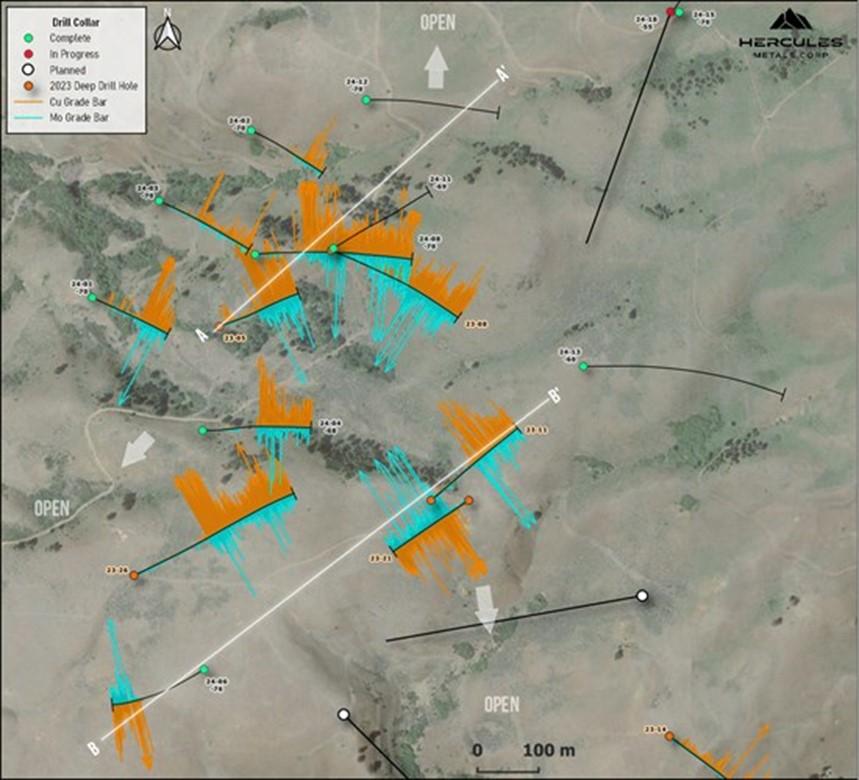
Figure 2: 1:6500 scale view of drill holes in Figure 1, showing section lines for Figures 3 and 4.
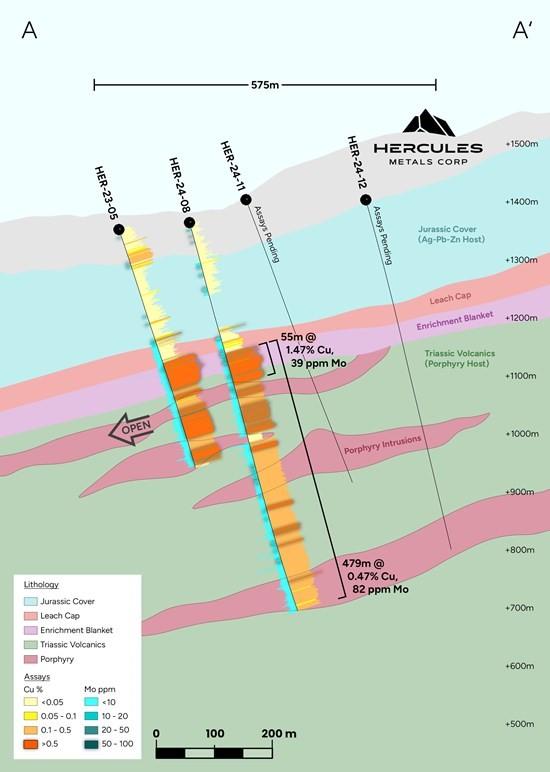
Figure 3: Cross-section A – A’ showing southwest dipping cover, erosional surface, leach cap and parallel enrichment blanket. The late porphyry dykes dip out of the page to the southeast, but have an apparent parallel dip as shown due to the orientation of the cross section.
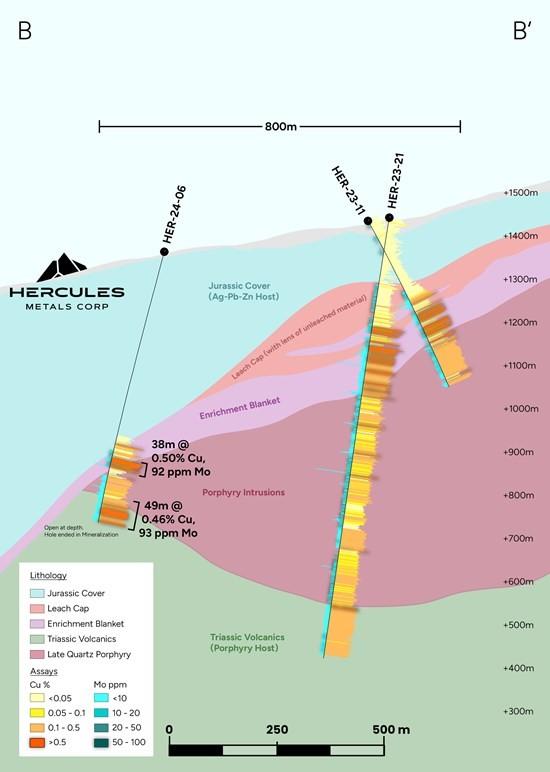
Figure 4: Cross-section B – B’ showing southwest-dipping unconformity. The thickest leach cap observed lies below 23-21, but pinches out by 24-06. The late porphyry thickens below 23-21 and dips out of the page to the southeast. The thickest bornite ever intercepted at Hercules occurs as a wedge of enrichment and possible relict potassic alteration above the late porphyry in 23-21. It was affected by leaching from above and therefore copper grades were not as high as other holes. It was then truncated by the late porphyry below. Planned holes will now test if the bornite wedge thickens down plunge to the southeast, as it departs from the thick leach cap and the top of the late porphyry dips deeper.
Spectral and Veining
Spectral readings taken throughout the porphyry system show a discernible pattern of increasing alteration temperature to the south and southeast. Drill holes HER-24-01 through -03, and 24-15 intersected low temperature phyllic and minor advanced argillic alteration, typical of the shallowest parts of a porphyry system. Veining in these holes is characterized by intense “D” vein stockworks, also typical of the margins of the system. Holes drilled to the south and southeast however intersect progressively higher temperature phyllic, and even observable relict potassic alteration. Densities of early quartz veins also increase in direct association with the increasing alteration temperatures. This pattern suggests that the Leviathan porphyry system has been tilted to the northwest.
Porphyry Intrusions
A quartz porphyry intrusion, interpreted to be a late phase of the porphyry system, is intersected in a number of drill holes. Preliminary modeling suggests a southeast plunging geometry, consistent with the interpretation that the system is tilted to the northwest. It also appears to pinch out to the northwest in a series of finger-like dykes. The late quartz porphyry is slightly grade dilutive relative to the volcanic wall rock, and drilling aims to target near its margins, or in its hanging wall, as it plunges off to the southeast. It should be noted that drilling has not yet identified the earliest porphyry intrusion, which is typically the highest grade and introduces the bulk of copper mineralization early in porphyry systems.
Drill Hole Summaries
HER-24-08 intersected strong mineralization in a 140-meter step-out northeast from 23-05. A trend of prospective mineralization has been noted from other holes drilled to the northeast, including HER-24-12. Additional drilling is warranted to test if the trend continues northeast of 24-12. Three core holes, HER-07, HER-24-09 and 24-09b, were lost in Jurassic cover, with HER-24-09 testing a step-out to the southwest of 23-05. Legacy’s RC drill will use the same pad to test the southwest extension of the trend. HER-24-12 did not intersect late quartz porphyry, which adds to the targets prospectivity.
HER-24-01 was drilled into a low temperature halo of D veining to the northwest, but also overlapped the margin of the enrichment blanket and graded 155m of 0.44% Cu and 11 g/t Ag, including 30m of 1.11% Cu and 48 g/t Ag.
HER-24-04 intersected late quartz porphyry, grading 0.33% Cu over 218m, including 57m of 0.54% Cu within the enrichment blanket.
HER-24-05 was drilled into a circular chargeability low and intersected a low-grade plug of late quartz porphyry, with trace copper sulfide. High barren quartz vein densities in the plug suggest a potential deep core may have been faulted in here.
HER-24-06 tested a chargeability high outside of HER-24-05 and encountered hypogene enrichment followed by a short interval of late porphyry. Copper grade increases after exiting late porphyry into biotite altered volcanics. A badly damaged post-mineral fault zone forced the hole to be terminated in 0.6% Cu.
Silver-Lead-Zinc in Jurassic Cover Sequence
Broad zones of disseminated silver-lead-zinc occur within the Hercules Rhyolite, an important unit of the Jurassic cover sequence. Although no longer the primary target, with commodities prices on the rise, the near surface silver mineralization may play an important role in potential future development scenarios.
Table 2: Silver-Lead-Zinc in Cover Sequence
| Hole ID | From (m) | To (m) | Interval (m) | Ag (g/t) | Pb (%) | Zn (%) | Pb+Zn (%) |
| HER-24-01 | 72.76 | 258.59 | 185.83 | 28.78 | .09 | .28 | 0.37 |
| including | 72.76 | 131.37 | 58.61 | 67.89 | .28 | .86 | 1.14 |
| including | 78.85 | 89.52 | 10.67 | 205.04 | 0.40 | 0.48 | 0.88 |
| HER-24-04 | 118.45 | 133.65 | 15.20 | 24.40 | 0.21 | 1.29 | 1.50 |
| HER-24-05 | 312.88 | 317.91 | 5.03 | 93.01 | – | – | – |
| HER-24-08 | 3.02 | 96.68 | 93.66 | 9.88 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.36 |
| including | 42.4 | 96.7 | 54.30 | 13.04 | 0.25 | 0.13 | 0.38 |
Table 3: Reported Drill Hole Locations
| Hole ID | Easting | Northing | Elevation | Depth (m) | Azimuth | Dip |
| HER-24-01 | 511023 | 4956683 | 1288 | 411.2 | 114.9 | -69.7 |
| HER-24-02 | 511283 | 4956956 | 1354 | 411.5 | 115.4 | -70.2 |
| HER-24-03 | 511132 | 4956841 | 1277 | 516.3 | 115.12 | -69.8 |
| HER-24-04 | 511203 | 4956466 | 1359 | 484.3 | 90.17 | -68.4 |
| HER-24-05 | 511237 | 4955710 | 1255 | 601.0 | 59.6 | -75.3 |
| HER-24-06 | 511206 | 4956076 | 1361 | 637.6 | 239.36 | -75.6 |
| HER-24-08 | 511289 | 4956754 | 1364 | 721.8 | 81.5 | -70.2 |
Sample Analysis and QAQC
All drill core samples were prepped and analyzed at MSA Labs in Langley, British Columbia, an ISO 17025 and ISO 9001 certified laboratory. Samples were dried and crushed to 2mm, from which a 250g sub-sample split was then pulverized to 85% passing a 75 micron sieve. Following preparation, assays were determined by the IMS-230 method. A 0.25g aliquot of the prepared pulp was digested in a 4-acid solution consisting of hydrochloric, nitric, perchloric and hydrofluoric acids. 4-acid is a near total digest and only the most highly resistant minerals are not dissolved. The resulting solution was analyzed via ICP-MS and ICP-ES for 48 elements and was corrected for inter-element spectral interferences. Lower detection limits for this procedure are 0.01 ppm for silver, 0.5 ppm for lead, 2 ppm for zinc, and 0.2 ppm for copper. Mercury is not reported due to volatilization in reaction with hydrofluoric acid and gold is not reported due to the small, 0.25g aliquot size being insufficient to overcome the nugget effect.
Gold was analyzed by FAS-111, a 30-gram fire assay fusion with AAS finish. No significant results were reported.
Samples with initial results beyond the upper detection limit of the IMS-230 method were analyzed by procedures ICF-6Ag, ICF-6Cu, ICF-6Pb and ICF-6Zn. The thresholds are 100 ppm for silver, and >1% for copper, lead and zinc.
MSA Labs employs internal quality control standards, duplicates and blank samples at set frequencies.
Blind certified reference materials (CRMs) and blank samples were systematically inserted by the Company into the sample stream and analyzed as part of the Company’s quality assurance/quality control protocol.
Qualified Person
The scientific and technical information in this news release has been reviewed and approved for disclosure by Christopher Longton BS, CPG, Hercules’ Vice President, Exploration. Mr. Longton is a “Qualified Person” for Hercules Metals within the meaning of National Instrument 43-101 – Standards of Disclosure for Mineral Projects.
About Hercules Metals Corp.
Hercules Metals Corp. is an exploration Company focused on developing Idaho’s newest copper and silver district.
The 100% owned Hercules Project located northwest of Cambridge, hosts the newly discovered Leviathan porphyry copper system, one of the most important discoveries in the region to date. The Company is well positioned for growth through continued drilling, supported by extensive historical and current exploration and a strategic investment by Barrick Gold.
With the potential for significant scale, the Company’s management and board of directors aims to build on its proven track record which includes the discovery and development of numerous precious metals projects worldwide.
MORE or "UNCATEGORIZED"
Eloro Resources Announces Closing of Bought Deal LIFE Private Placement for Gross Proceeds of C$17 Million
Eloro Resources Ltd. (TSX: ELO) (FSE: P2QM) is pleased to announce the closing of its previously an... READ MORE
Minera Alamos Updates Resources and Reserves for the Pan Gold Mine in Nevada
Minera Alamos Inc. (TSX-V: MAI) (OTCQX: MAIFF) is pleased to announce updated Mineral Resource and M... READ MORE
Ero Copper Reports Fourth Quarter and Full Year 2025 Operating and Financial Results
Ero Copper Corp. (TSX: ERO) (NYSE: ERO) is pleased to announce its operating and financial results f... READ MORE
Rare Element Resources Announces Results of Oversubscribed Rights Offering of Common Shares
Rare Element Resources Ltd. (OTCQB: REEMF) is pleased to report that its previously announced... READ MORE
TRX Gold Reports Record Q2 2026 Production and Company Update
TRX Gold Corporation (TSX: TRX) (NYSE American: TRX) is pleased to announce preliminary resu... READ MORE