Canada Nickel Announces Positive Bankable Feasibility Study For its Crawford Nickel Sulphide Project
Highlights
- $2.5 billion after-tax NPV8% and IRR of 17.1%; increasing to $2.6 billion after-tax NPV8% and IRR of 18.3% with projected Carbon Capture & Storage tax credits
- Crawford is world’s 2nd largest nickel reserve and 2nd largest resource1. Initial mineral reserve of 1.7 billion tonnes of ore grading 0.22% nickel
- Production of 1.6 million tonnes nickel, 24 kt cobalt, 490 koz palladium & platinum, 58 million tonnes iron and 2.8 million tonnes chromium over 41-year project life
- Annual EBITDA of $811 million, free cash flow (FCF) of $546 million, and 48ktpa of nickel production during peak 27-year period
- One of Canada’s largest carbon storage facilities with 1.5 Mtpa carbon captured and stored during peak 27-year period
- Crawford is a net negative contributor to global CO2 footprint – with 30 tonnes of carbon capture and storage capacity per tonne of nickel remaining after accounting for project footprint
(All amounts in US dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
Canada Nickel Company Inc. (TSX-V: CNC) (OTCQX: CNIKF) released results from the Bankable Feasibility Study for its innovative and wholly-owned Crawford Nickel Sulphide Project, confirming significantly improved economics from its Preliminary Economic Analysis (“PEA”), with an after-tax NPV8% of $2.5 billion and IRR of 17.1%. The BFS was prepared by Ausenco Engineering Canada Inc. in accordance with National Instrument 43-101.
Crawford, located in Timmins, Ontario, Canada, is the world’s second largest nickel reserve1. Once in production, it is also expected to become one of Canada’s largest carbon storage facilities and be a net negative contributor of CO2 over the project life.
Mark Selby, CEO of Canada Nickel, said, “This bankable feasibility study is a significant milestone for Crawford and a major step forward in demonstrating the value of our Timmins Nickel District and its potential to anchor a Zero Carbon Industrial Cluster in the Timmins-Cochrane region. Crawford is poised to be a leader in the energy transition through the large-scale production of critical minerals, including nickel and cobalt, and is expected to become the sole North American producer of chromium2, while also supporting Canada’s climate objectives through industrial-scale carbon capture and storage.”
| ________________________________ |
| 1 Source: Wood Mackenzie, Nickel Cost Service Q3 2023 data |
| 2 Source U.S. Geological Survey, Mineral Commodity Summaries, Chromium January 2023 |
Mr. Selby continued, “I am very proud of our team for accomplishing this milestone in a very short `of time. Just four years ago, Crawford had only five drill holes. Today, we believe it is a world-class project with tremendous momentum. We are fully focused on pursuing our next milestones of obtaining permits, developing a financing package, and moving towards a production decision by mid-2025, with a goal of first production by the end of 2027.”
Crawford 2023 BFS Highlights
- Robust economics
- After-tax, $2.5 billion NPV8% and 17.1% IRR; increasing to $2.6 billion NPV8% and 18.3% IRR with projected Carbon Capture and Storage tax credits
- Large initial mineral reserve anchored by significantly larger mineral resource
- Proven & Probable reserves of 3.8 million tonnes contained nickel from 1.7 billion tonnes ore grading 0.22% nickel make Crawford the world’s 2nd largest nickel reserve3. Reserves are hosted in a Measured & Indicated resource which increased by 74% (compared to the 2022 resource estimate) to 6.0 million tonnes. With additional Inferred mineral resources of 3.7 million tonnes contained nickel, Crawford is the world’s 2nd largest nickel resource3.
- Large scale, low cost, long-life
-
- Annual average nickel production of 83 million pounds (38k tonnes) over a 41-year life, with production of 48 ktpa nickel, 0.8 ktpa cobalt, 13 koz palladium and platinum, 1.6 Mtpa iron and 76 ktpa chrome over 27-year peak period
- Net life-of-mine C1 cash cost of $0.39/lb nickel (by-product basis) place Crawford in the first quartile of the cost curve3. The net AISC cost, on a by-product basis, is $1.21/lb nickel.
- Projected revenue exceeds $48 billion, or more than $1 billion annually over project life.
- Significant improvement in recoveries from PEA:
- Nickel: 10% improvement life-of-mine (41% versus 37% used in PEA), and a 23% improvement in Phase I/Phase II compared to PEA (46% versus 37% in the PEA)
- Improvements to life of mine recovery for Iron: 46%, Cobalt: 38%, and Chrome: 5%
- Significant earnings and free cash flow generation
- Projected annual EBITDA of $810 million and FCF of $540 million over peak period, annual EBITDA of $667 million and FCF of $431 million over project life
- Minimization of carbon footprint
- Minimal carbon footprint of 4.8 tonnes CO2/ tonne of nickel in concentrate,2.3 tonnes CO2/tonne of nickel equivalent 4(“NiEq”); largely due to electrically powered mining fleet, including trolley-assist trucks, that are expected to reduce diesel consumption by over 40% compared to diesel powered equipment.
- Implementation of the Company’s proprietary IPT (In-Process Tailings) Carbonation process is anticipated to allow capture and storage of 1.5 million tonnes CO2 annually during 27-year peak period, the bulk of which will be sold to third parties.
- Anticipated net negative carbon footprint from carbon capture and storage capacity of 30 tonnes CO2 / tonne of nickel after accounting for project footprint
| _______________________________ | |
| 3 | Source: Wood Mackenzie, Nickel Cost Service Q3 2023 data |
| 4 | Nickel equivalent using prices of $21,000/t Ni, $40,000/t Co, $1,350/oz Pd, $1,150/oz Pt, $325/t Fe (equivalent to $89/t iron ore price) and $3,860/t Cr; metallurgical recoveries based on average of 41% Ni, 11% Co, 48% Pd, 22% Pt, 53% Fe, 28% Cr. |
Crawford BFS Summary
Crawford will be a conventional open pit mine/mill operation constructed in two phases. The initial phase, costing $1.9 billion, will have a mill throughput of 60 ktpd. The second phase, planned for commissioning during the fourth year following 24 months construction, will double mill throughput to 120 ktpd at a cost of $1.6 billion. The third phase occurs after the pits have been depleted in Year 30 and the 120 ktpd milling rate is satisfied from stockpiled lower grade ore.
Crawford Bankable Feasibility Study Results
| Mining & Milling |
Unit |
Construction |
Phase 1 |
Phase 2 |
Phase 3 |
LOM |
||
| Duration | 2.5 years | 3.5 years | 26.5 years | 11.25 years | 41.25 years | |||
| Mill Capacity | Ktpd | 0 | 60 | 120 | 120 | 120 | ||
| Total Mined | Mt | 103 | 423 | 5,181 | 0 | 5,707 | ||
| Ore Mined | Mt | 14 | 125 | 1,575 | 0 | 1,715 | ||
| Ore Milled | Mt | 0 | 73 | 1,157 | 485 | 1,715 | ||
| Strip Ratio | Waste : Ore Mined | 6.17 | 2.37 | 2.29 | n/a | 2.33 | ||
|
Grade |
||||||||
| Nickel Head Grade | % | 0.26 | 0.24 | 0.17 | 0.22 | |||
| Cobalt Head Grade | % | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.012 | 0.013 | |||
| Palladium & Platinum Head Grade | g/t | 0.030 | 0.024 | 0.021 | 0.024 | |||
| Iron Head Grade | % | 6.20 | 6.43 | 6.49 | 6.44 | |||
| Chromium Head Grade | % | 0.63 | 0.60 | 0.49 | 0.57 | |||
|
Recovery |
||||||||
| Nickel Recovery | % | 48 % | 46 % | 25 % | 41 % | |||
| Cobalt Recovery | % | 19 % | 14 % | 4 % | 11 % | |||
| Palladium & Platinum Recovery | % | 40 % | 39 % | 33 % | 38 % | |||
| Iron Recovery | % | 54 % | 56 % | 46 % | 53 % | |||
| Chromium Recovery | % | 28 % | 29 % | 26 % | 28 % | |||
|
Annual Production
|
||||||||
| Recovered Nickel | Ktpa | 26 | 48 | 18 | 38 | |||
| Recovered Cobalt | Ktpa | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.6 | |||
| Recovered Palladium & Platinum | Kozpa | 8 | 13 | 10 | 12 | |||
| Recovered Iron | Mtpa | 0.7 | 1.6 | 1.3 | 1.4 | |||
| Recovered Chromium | Ktpa | 37 | 76 | 54 | 67 | |||
| Carbon Capture | Mtpa | 0.6 | 1.5 | 1.1 | 1.3 | |||
|
Revenue & Costs |
||||||||
| NSR | US$ / tonne milled | $34.96 | $32.31 | $16.96 | $28.08 | |||
| Mining Opex | US$ / tonne milled | $9.82 | $6.21 | $0.62 | $4.78 | |||
| Milling Opex | US$ / tonne milled | $5.31 | $5.18 | $5.19 | $5.19 | |||
| G&A Opex | US$ / tonne milled | $2.35 | $1.00 | $0.50 | $0.92 | |||
| Total Onsite Costs | US$ / tonne milled | $17.48 | $12.38 | $6.31 | $10.88 | |||
| Gross C1 Cash Cost | US$ / lb NiEq | $4.82 | $3.72 | $3.64 | $5.96 | |||
| Net C1 Cash Cost | US$ / lb Ni | $2.67 | $0.68 | ($2.39) | $0.39 | |||
| Net AISC | US$ / lb Ni | $2.96 | $1.54 | ($1.72) | $1.21 | |||
| Total Investment | US$ millions | $1,946 | $1,602 | $1,450 | $159 | $5,157 | ||
|
Cash Flow |
||||||||
| Annual EBITDA | US$ millions | $0 | $349 | $811 | $426 | $667 | ||
| Annual Free Cash Flow | US$ millions | ($723) | $17 | $545 | $291 | $431 | ||
The Base Case economics includes the Critical Minerals Investment Tax Credit, that was outlined during the 2023 federal budget presentation. While it is anticipated that Crawford would also qualify for the Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage ITC, this will be included as an opportunity until approval to receive the credit has been obtained.
The after-tax project returns are robust: $2.5 billion NPV8% and 17.1% IRR; increasing to $2.6 billion NPV8% and 18.3% IRR with projected Carbon Capture and Storage tax credits. Overall payback is 5.6 years and peak capital requirement to build both phases is $1.7 billion, less than initial capital cost estimate of $1.9 billion because of the inclusion of the Critical Minerals ITC. Government tax credits are expected to exceed $1 billion over the project life for the scenario which includes both the Critical Minerals and expected Carbon Capture tax credits.
Mining
Crawford will mine two separate open pits that contain approximately equal tonnages of ore. Mine production rates have been decoupled from the mill, resulting in a 30-year mine life compared to 41 years for the overall project. While there is an initial cost associated with stockpiling lower grade ore, economic impacts are anticipated to be more than offset by treating higher grade ore in the early years and accelerating cashflows. This strategy also allows for in-pit deposition of tailings after the first pit has been depleted in Year 17. Over the life of project, 61% of total tailings production will be impounded in-pit, significantly reducing Crawford’s surficial and environmental footprint while reducing the cost of impoundment.
Approximately 89% of material mined will be rock, which will be drilled and blasted before being loaded by electrically powered rope shovels or large hydraulic excavators into 290 tonne trucks equipped with trolley assist. Over 70% of uphill hauls by this fleet will be traveled on trolley, reducing diesel consumption by approximately 1.5 billion litres while faster speeds will reduce the fleet by 12 units. The remaining material will be overburden that will not require drilling and blasting and will be loaded and hauled with a mixed fleet of smaller equipment.
Mineral Processing
The concentrator will process ore using a conventional milling circuit. Unit operations include crushing, semi-autogenous and ball mill grinding, desliming, nickel flotation, magnetic separation on the flotation tailings and carbon storage using the Company’s proprietary IPT Carbonation technology. The BFS flowsheet has been optimized from the PEA and is expected to deliver improved recoveries of all base metals, improved concentrate grades, as well as large scale carbon storage.
Comparison of Key Metrics for BFS vs PEA
|
Crawford FS |
Crawford |
Variance: FS vs PEA |
||||||
|
Mining & Milling |
units |
Phase1 -2 |
LOM |
PEA |
Phase1 -2 |
LOM |
||
| Life | years | 30 | 41 | 25 | +20 % | +64 % | ||
| Ore Mined | Mt | 1,700 | 1,715 | 907 | +87 % | +89 % | ||
| Ore Milled | Mt | 1,230 | 1,715 | 907 | +36 % | +89 % | ||
|
Recovery |
||||||||
| Nickel Recovery | % | 46 % | 41 % | 37 % | +23 % | +10 % | ||
| Cobalt Recovery | % | 14 % | 11 % | 8 % | +69 % | +38 % | ||
| Palladium & Platinum Recovery | % | 39 % | 38 % | n/a | ||||
| Iron Recovery | % | 56 % | 53 % | 36 % | +54 % | +46 % | ||
| Chromium Recovery | % | 29 % | 28 % | 27 % | +8 % | +5 % | ||
|
Annual Production |
||||||||
| Recovered Nickel | Ktpa | 45 | 38 | 34 | +33 % | +12 % | ||
| Recovered Cobalt | Ktpa | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.4 | +89 % | +55 % | ||
| Recovered Palladium & Platinum | Kozpa | 13 | 12 | n/a | ||||
| Recovered Iron | Mtpa | 1.5 | 1.4 | 0.9 | +70 % | +65 % | ||
| Recovered Chromium | Ktpa | 71 | 67 | 59 | +22 % | +14 % | ||
| Carbon Storage | Mtpa | 1.4 | 1.3 | n/a | ||||
Crawford will produce two concentrates with life-of-mine average concentrate grades as follows:
- Nickel concentrate: 34% nickel, 0.7% cobalt and 4.1 g/t combined Palladium and Platinum
- Iron ore concentrate: 55% iron, 0.3% nickel, 2.6% chromium
It is believed the nickel concentrate is believed to be the highest-grade concentrate in the global market and thus has a wide range of potential markets, including both the stainless steel and the battery metal sector. The iron ore concentrate contains three of the key ingredients for 300 series stainless and alloy steel market and it is expected to be a suitable direct feed for North American production of that product.
IPT Carbonation
Crawford, and the Company’s other properties in the Timmins Nickel District, are hosted in ultramafic rock, which contain minerals such as brucite that naturally absorb and sequester CO2. Canada Nickel has developed the novel IPT Carbonation process which involves injecting a concentrated source of CO2 into tailings generated by the milling process for a brief period of time. This simple process stores CO2 chemically in the tailings while they are still in the processing circuit, rather than after they have been finally deposited. The interest already received from multiple large multinational companies pursuing carbon storage solutions further supports the Company’s belief that this process is expected to be an effective carbon storage approach that would meet Environment and Climate Change Canada requirements to allow the Company to utilize the CCUS ITC.
Location & Infrastructure
Crawford is located within an established mining camp, approximately 40 kilometres north of Timmins. The project thus has access to infrastructure that has been developed over the past century to service the industry’s requirements including, but not limited to, energy, water, equipment, logistics and skilled human resources.
Crawford will require connection to the electrical grid. Canada Nickel has entered into an agreement with a local First Nations service provider, Transmission Infrastructure Partnerships 1 5, that will be responsible for costs, executing the work and powerline maintenance. These costs will be recovered from Crawford over a 25-year period.
Other infrastructural requirements form part of the project scope, including those related to the realignment of Highway 655 and a 500kV power line, which currently cross the property. The realignment will total approximately 27.5 kilometres. A portion of this distance will be equipped with a new rail spur that will facilitate delivery of consumables to, and shipment of concentrates from Crawford.
| _______________________________ |
| 5 See Canada Nickel press release dated December 16, 2020 |
Mineral Resources
Crawford’s Measured and Indicated Resources with an effective date of August 31, 2023 have grown by 74% since the previous resource update in May 2022 (mineral resources are inclusive of reserves).
| Tonnage | Grade | Contained Metal | |||||||||||||||
| (Mt) | Ni (%) | Co (%) | Pd (g/t) | Pt (g/t) | Fe (%) | Cr (%) | Bruc (%) | Ni (kt) | Co (kt) | Pd (koz) | Pt (koz) | Fe (Mt) | Cr (kt) | ||||
|
Higher Grade Main Zone |
|||||||||||||||||
| Measured | 253 | 0.30 | 0.013 | 0.027 | 0.012 | 6.40 | 0.59 | 1.73 | 770 | 33 | 219 | 96 | 16.2 | 1,503 | |||
| Indicated | 296 | 0.28 | 0.013 | 0.023 | 0.012 | 6.93 | 0.57 | 1.36 | 830 | 39 | 218 | 112 | 20.5 | 1,694 | |||
| Mea+Ind | 549 | 0.29 | 0.013 | 0.025 | 0.012 | 6.68 | 0.58 | 1.53 | 1,600 | 72 | 437 | 207 | 36.7 | 3,197 | |||
| Inferred | 212 | 0.28 | 0.013 | 0.018 | 0.011 | 6.91 | 0.56 | 1.21 | 587 | 28 | 123 | 73 | 14.6 | 1,190 | |||
|
Lower Grade Main Zone |
|||||||||||||||||
| Measured | 280 | 0.22 | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.009 | 6.89 | 0.59 | 1.15 | 607 | 37 | 96 | 79 | 19.3 | 1,646 | |||
| Indicated | 698 | 0.21 | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.009 | 7.10 | 0.57 | 1.07 | 1,465 | 92 | 249 | 207 | 49.6 | 3,998 | |||
| Mea+Ind | 978 | 0.21 | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.009 | 7.04 | 0.58 | 1.10 | 2,072 | 129 | 346 | 285 | 68.9 | 5,644 | |||
| Inferred | 1324 | 0.21 | 0.013 | 0.010 | 0.009 | 7.20 | 0.57 | 0.94 | 2,772 | 174 | 420 | 386 | 95.4 | 7,544 | |||
|
Higher Grade East Zone |
|||||||||||||||||
| Measured | 394 | 0.26 | 0.012 | 0.015 | 0.009 | 5.92 | 0.65 | 3.10 | 1,022 | 49 | 185 | 119 | 23.3 | 2,546 | |||
| Indicated | 300 | 0.26 | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.007 | 5.85 | 0.63 | 3.19 | 774 | 38 | 103 | 69 | 17.5 | 1,887 | |||
| Mea+Ind | 694 | 0.26 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.008 | 5.89 | 0.64 | 3.14 | 1,795 | 87 | 287 | 188 | 40.9 | 4,432 | |||
| Inferred | 112 | 0.26 | 0.013 | 0.010 | 0.007 | 5.90 | 0.62 | 2.89 | 289 | 14 | 37 | 25 | 6.6 | 695 | |||
|
Lower Grade East Zone
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Measured | 169 | 0.16 | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.009 | 7.25 | 0.54 | 0.40 | 279 | 21 | 57 | 49 | 12.3 | 908 | |||
| Indicated | 172 | 0.17 | 0.012 | 0.011 | 0.009 | 7.11 | 0.52 | 0.93 | 289 | 21 | 61 | 52 | 12.2 | 886 | |||
| Mea+Ind | 341 | 0.17 | 0.012 | 0.011 | 0.009 | 7.18 | 0.53 | 0.67 | 568 | 43 | 119 | 102 | 24.5 | 1,794 | |||
| Inferred | 45 | 0.17 | 0.013 | 0.010 | 0.008 | 7.11 | 0.54 | 0.55 | 78 | 6 | 14 | 12 | 3.2 | 244 | |||
| Total Crawford Resource | |||||||||||||||||
| Mea+Ind |
2562 |
0.24 |
0.013 |
0.014 |
0.010 |
6.67 |
0.59 |
1.69 |
6,035 |
330 |
1,189 |
783 |
170.9 |
15,066 |
|||
| Inferred |
1693 |
0.22 |
0.013 |
0.011 |
0.009 |
7.08 |
0.57 |
1.09 |
3,726 |
222 |
594 |
496 |
119.9 |
9,674 |
|||
Mineral Resources have an effective date of August 31, 2023. Mr Scott Jobin-Bevans with Caracle Creek International Consulting Inc at the time of preparation of the estimate, is the Qualified Person responsible for the Mineral Resource Estimate. Mineral Resources are inclusive of Mineral Reserves. Mineral Resources are not Mineral Reserves and do not have demonstrated economic viability. Mineral resources are contained within a Lerchs-Grossmann pit shell using prices of $20,000/t nickel, $48,500/t cobalt, $1350/oz palladium, $1,150/oz platinum, $290/t iron (equivalent to $80/t iron ore price) and $2,290/t chromium; metallurgical recoveries based on test work, open pit mining costs ranging from C$1.35 – C$3.17/t mined, depending upon depth and size of equipment, mill + G&A costs of C$7.54/t milled and royalties to 4.1% of NSR. The QP is not aware of any environmental, permitting, legal, title, taxation, socio‐economic, marketing, political, or other relevant issues that could potentially affect this Mineral Resource Estimate.
Mineral Reserves
Mineral reserves are contained within an engineered pit design that has been based on a Lerchs-Grossmann pit optimization run at a Revenue Factor (RF) 65% of the base case prices; or $13,650/t Ni, $26,000/t Co, $58/t iron ore, $2,500/t Cr, $878/oz Pd and $748/oz Pt. Mineral reserves include unplanned dilution of 0.4%
Mineral Reserves Statement (effective date Aug 31 2023)
| Ore | Grade | Contained Metal | Mt CO2 | |||||||||||||||
| (Mt) | Ni % | Co % | Pd g/t | Pt g/t | Fe % | Cr % | Bruc % | Ni (kt) | Co (kt) | Pd (koz) | Pt (koz) | Fe (Mt) | Cr (kt) | Capture | ||||
|
HG Main Zone |
||||||||||||||||||
| Proven | 208 | 0.31 | 0.013 | 0.027 | 0.011 | 6.23 | 0.60 | 1.78 | 641 | 27 | 180 | 74 | 13 | 1,249 | 8 | |||
| Probable | 64 | 0.29 | 0.013 | 0.023 | 0.012 | 6.47 | 0.54 | 1.98 | 185 | 8 | 47 | 24 | 4 | 348 | 3 | |||
|
LG Main Zone |
||||||||||||||||||
| Proven | 213 | 0.21 | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.009 | 6.69 | 0.58 | 1.15 | 445 | 27 | 75 | 58 | 14 | 1,226 | 6 | |||
| Probable | 368 | 0.18 | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.009 | 6.82 | 0.53 | 1.03 | 678 | 47 | 133 | 106 | 25 | 1,961 | 10 | |||
|
HG East Zone |
||||||||||||||||||
| Proven | 375 | 0.26 | 0.012 | 0.014 | 0.009 | 5.92 | 0.64 | 2.84 | 965 | 47 | 170 | 112 | 22 | 2,418 | 18 | |||
| Probable | 148 | 0.25 | 0.012 | 0.009 | 0.007 | 5.83 | 0.63 | 2.87 | 369 | 18 | 44 | 32 | 9 | 926 | 7 | |||
|
LG East Zone |
||||||||||||||||||
| Proven | 198 | 0.15 | 0.012 | 0.011 | 0.011 | 7.00 | 0.50 | 0.32 | 295 | 24 | 73 | 67 | 14 | 998 | 1 | |||
| Probable | 141 | 0.15 | 0.011 | 0.012 | 0.010 | 6.54 | 0.47 | 0.60 | 212 | 16 | 53 | 46 | 9 | 659 | 2 | |||
|
Total Crawford |
||||||||||||||||||
| Proven | 994 | 0.24 | 0.013 | 0.016 | 0.010 | 6.37 | 0.59 | 1.75 | 2,345 | 125 | 498 | 311 | 63 | 5,892 | 33 | |||
| Probable | 721 | 0.20 | 0.012 | 0.012 | 0.009 | 6.53 | 0.54 | 1.41 | 1,444 | 89 | 278 | 208 | 47 | 3,895 | 22 | |||
|
Proven + Probable |
1,715 |
0.22 |
0.013 |
0.014 |
0.009 |
6.44 |
0.57 |
1.61 |
3,789 |
215 |
777 |
519 |
110 |
9,787 |
54 |
|||
The Mineral Reserve Estimate was prepared in accordance with CIM Definition Standards for Mineral Resources and Mineral Reserves (CIM, 2014) by QP Dave Penswick, P.Eng who is an independent consultant. Mineral Reserves are included within the reported Mineral Resources. Mineral reserves are contained within a Lerchs-Grossmann pit shell using prices of $15,650/t nickel, $26,000/t cobalt, $878/oz palladium, $748/oz platinum, $211/t iron (equivalent to $58/t iron ore price) and $2,500/t chromium; metallurgical recoveries based on test work, open pit mining costs ranging from C$1.35 – C$3.17/t mined, depending upon depth and size of equipment, mill + G&A costs of C$7.54/t milled and royalties to 4.1% of NSR. The QP is not aware of any environmental, permitting, legal, title, taxation, socio‐economic, marketing, political, or other relevant issues that could potentially affect this Mineral Resource Estimate.
Crawford is now the world’s 2nd largest nickel reserve 6.
Capital Cost
|
Total Capital |
units |
Phase 1 |
Phase 2 |
Sustaining |
LOM | ||
| Mining | US$ millions | $499 | $420 | $1,304 | $2,222 | ||
| Process Plant | US$ millions | $721 | $726 | $0 | $1,447 | ||
| TMF & Water Management | US$ millions | $98 | $84 | $103 | $285 | ||
| Infrastructure | US$ millions | $205 | $93 | $74 | $372 | ||
| Indirects | US$ millions | $235 | $132 | $0 | $367 | ||
| Contingency | US$ millions | $185 | $145 | $0 | $330 | ||
| Closure and Other | US$ millions | $0 | $0 | $134 | $134 | ||
| Total | US$ millions | $1,943 | $1,600 | $1,615 | $5,157 | ||
| Notes: | |||||||
| 1. Indirect Costs for Process Plant only. Indirect costs for Mining, Off-Site Infrastructure and TMF within those areas | |||||||
The bankable feasibility study capital cost estimates are consistent with AACE Class 3 standards and include an allowance for growth averaging 6% within the direct estimate of applicable construction activities. In addition, a contingency averaging 11% has been applied to all direct and indirect items in the two phases of the project.
The capital estimate does not include escalation or interest.
| ______________________________ |
| 6 Source: Wood Mackenzie, Nickel Cost Service Q3 2023 data |
Operating Cost
|
Operating Cost |
units |
Phase1 |
Phase2 |
Phase3 |
LOM |
|
| Labour | average FTE1 | 1,057 | 851 | 305 | 720 | |
| Labour | US$/t milled | $4.36 | $1.74 | $0.60 | $1.53 | |
| Consumables | US$/t milled | $4.12 | $3.70 | $2.41 | $3.35 | |
| Maintenance | US$/t milled | $2.64 | $2.19 | $0.65 | $1.78 | |
| Fuel | US$/t milled | $1.90 | $1.26 | $0.09 | $0.96 | |
| Power | US$/t milled | $2.47 | $2.62 | $2.24 | $2.50 | |
| Other | US$/t milled | $1.97 | $0.87 | $0.31 | $0.76 | |
| TOTAL | US$/t milled | $17.47 | $12.38 | $6.31 | $10.88 | |
| Note: 1. Full Time Equivalent |
||||||
Operating costs were developed using a zero-based model and benchmarked against existing operations. Crawford will achieve low labour costs through the benefits of scale and utilization of proven technologies, such as trolley-assisted truck haulage. These technologies will also keep expenditure on fuel low. As a result of Crawford’s low site costs, it is expected the EBITDA margin will average 57% over the life of project. It is expected that Crawford will also be positioned in the lower half of the first quartile of Net C1 Cash Costs.
Source: Wood Mackenzie, Nickel Cost Service Q3 2023 data
Long-term price Assumptions (2023 real basis)
- Ni Price: $21,000/t ($9.53 /lb)
- Co Price: $40,000/t ($18.14 / lb)
- Pd Price: $1,350/oz
- Pt Price: $1,150/oz
- Iron Price: $325/t (equivalent to iron ore price of $89/t)
- Chromium Price: $3,860/t ($1.75/lb)
- C$:$US: $0.76
- Oil Price: $70/bbl
Sensitivities
|
Delta NPV 8% ($ MM) |
Delta IRR (%) |
Delta Net C1 Cash Cost ($/lb) |
||||||
|
Item |
+10 % |
-10 % |
+10 % |
-10 % |
+10 % |
-10 % |
||
| Nickel Price ± 10% ($18,900 – $23,100) | $508 | ($504) | 1.8 % | (1.8 %) | $0.00 | $0.00 | ||
| Iron Price ± 10% ($80 – $98) | $142 | ($141) | 0.5 % | (0.5 %) | ($0.30) | $0.30 | ||
| Chrome Price ± 10% ($3,474 – $4,246) | $108 | ($106) | 0.4 % | 0.4 % | ($0.22) | $0.22 | ||
| Cobalt Price ± 10% ($36,000 – $44,000) | $12 | ($12) | 0.0 % | (0.0 %) | ($0.02) | $0.02 | ||
| Oil Price ± 10% ($63 – $77) | ($44) | $44 | (0.2 %) | 0.2 % | $0.06 | ($0.06) | ||
| Nickel Recovery ± 10% (37% – 45%) | $505 | ($501) | 1.8 % | (1.8 %) | ($0.03) | $0.04 | ||
| Initial Capex ± 10% | ($99) | $101 | (0.8 %) | 1.0 % | $0.00 | $0.00 | ||
| Expansion Capex ± 10% | ($39) | $42 | (0.3 %) | 0.3 % | $0.00 | $0.00 | ||
| Opex ± 10% | ($339) | $343 | (1.2 %) | 1.3 % | $0.60 | ($0.60) | ||
Returns are most sensitive to a variation in the price or recovery of nickel, with a 10% variation in price leading to a 20% variation in NPV, or 2.0x the variation to input. Returns are also sensitive to operating costs, at 1.4x the variation to input. Returns are less sensitive to the iron or chrome prices, at 0.6x and 0.4x the variation to input, respectively. Returns are relatively insensitive to variation in the cobalt price while variation in palladium or platinum prices has less than a 0.1% impact on NPV. The sensitivity to initial capex (0.4x input) is double that of expansion capex (0.2x), which equals the sensitivity to fuel prices.
Next Steps
In parallel with the completion of the BFS, Canada Nickel is actively pursuing the work needed to obtain all necessary federal and provincial permits, and to develop a financing package with its advisors Scotiabank, Deutsche Bank, and Cutfield Freeman by mid-2025. This would be followed by a decision to initiate construction of Crawford with a target of first production by end 2027. In order to support this process and as part of its intention to responsibly originate materials to power the energy transition, Canada Nickel will use the BFS results to feed its ongoing innovative engagement strategy focussed on fostering meaningful and productive relationships with its Indigenous partners as well as with the surrounding communities. A technical report in support of the BFS will be filed with the Canadian securities regulatory authorities on SEDAR+ within 45 days of this news release.
Qualified Person
In Stephen J. Balch P.Geo. (ON), VP Exploration of Canada Nickel and a “qualified person” as such term is defined by National Instrument 43-101, has verified the data disclosed in this news release, and has otherwise reviewed and approved the technical information in this news release on behalf of Canada Nickel.
About Canada Nickel
Canada Nickel Company Inc. is advancing the next generation of nickel-sulphide projects to deliver nickel required to feed the high growth electric vehicle and stainless steel markets. Canada Nickel Company has applied in multiple jurisdictions to trademark the terms NetZero Nickel™, NetZero Cobalt™ and NetZero Iron™ and is pursuing the development of processes to allow the production of net zero carbon nickel, cobalt, and iron products. Canada Nickel provides investors with leverage to nickel in low political risk jurisdictions. Canada Nickel is currently anchored by its 100% owned flagship Crawford Nickel-Cobalt Sulphide Project in the heart of the prolific Timmins-Cochrane mining camp.
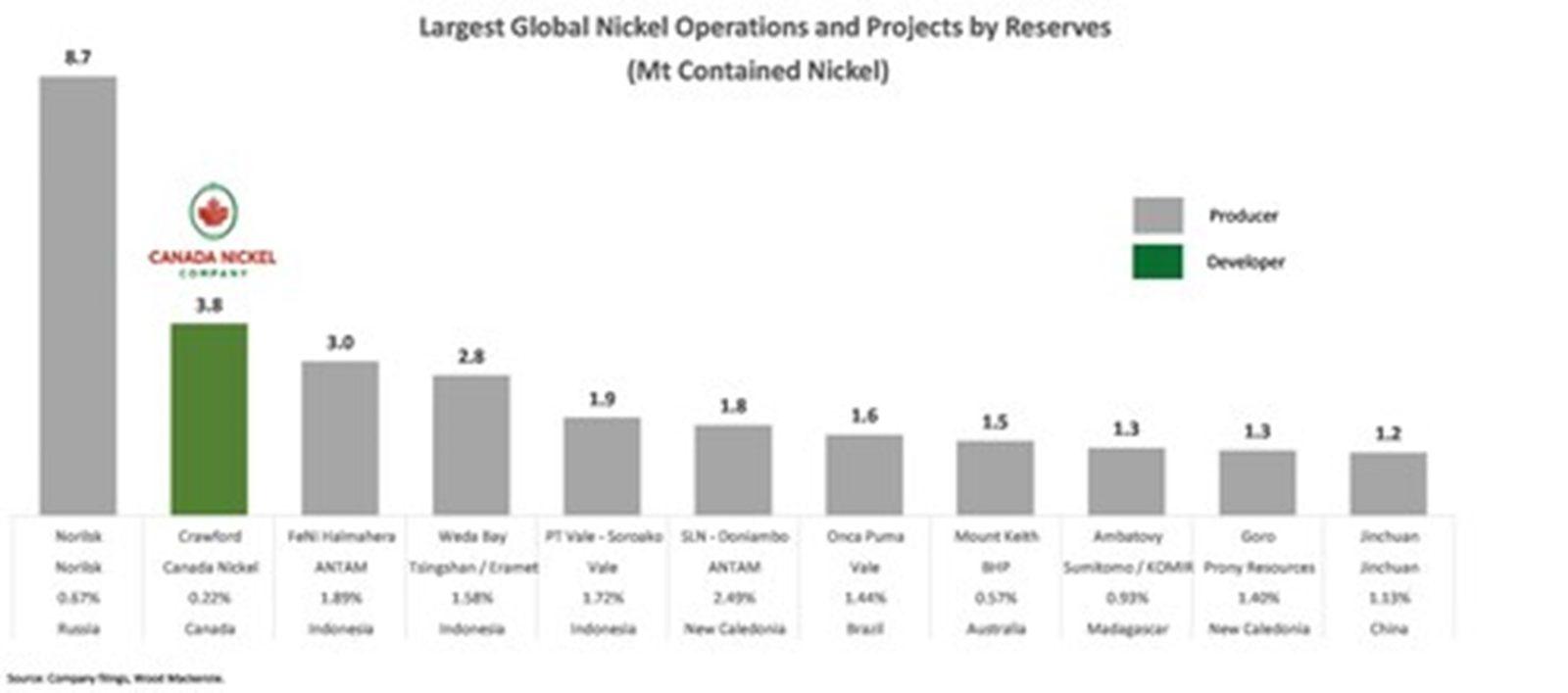
Crawford is now the world’s 2nd largest nickel reserve 6 (CNW Group/Canada Nickel Company Inc.)
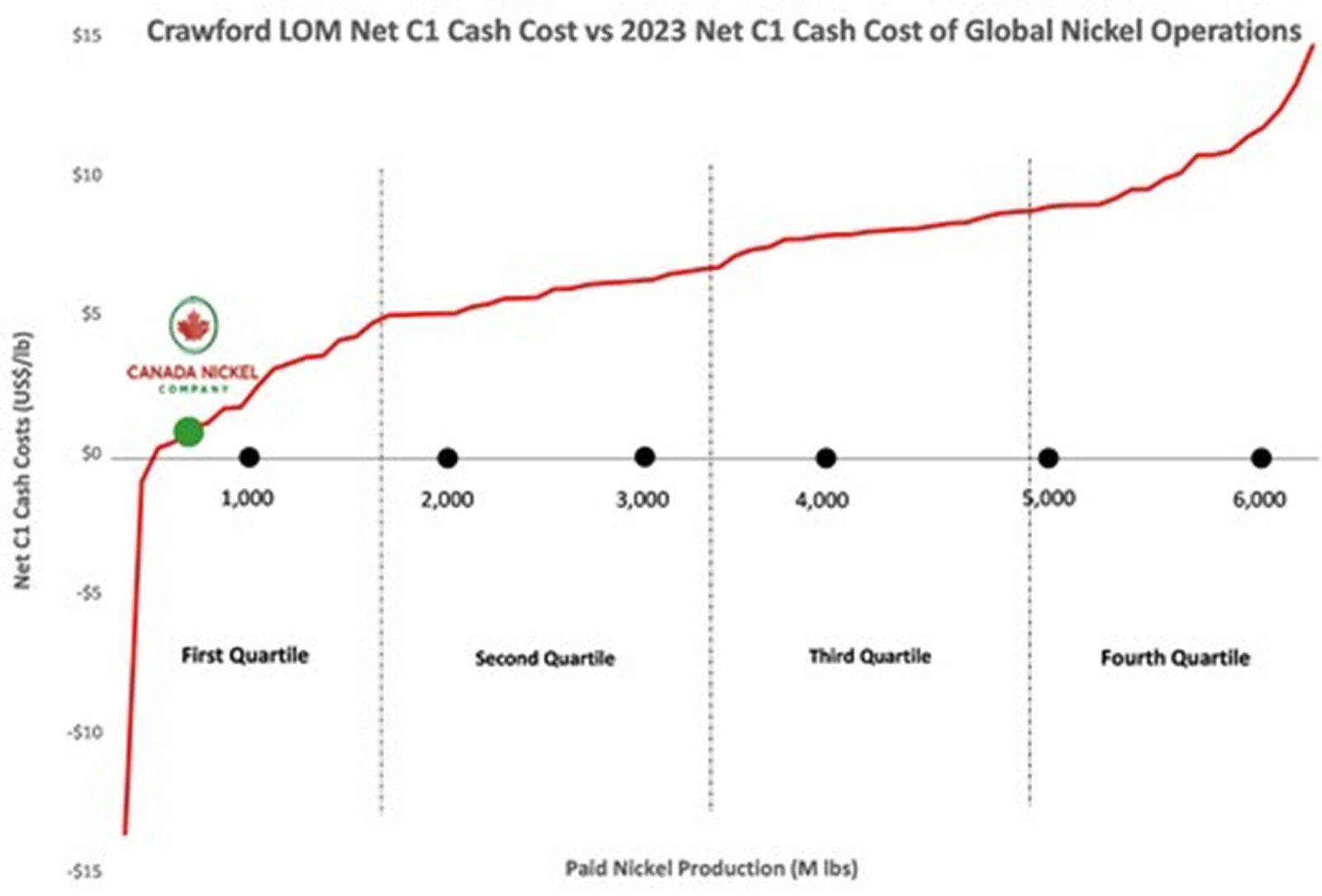
Fig.2 (CNW Group/Canada Nickel Company Inc.)
MORE or "UNCATEGORIZED"
Eloro Resources Announces Closing of Bought Deal LIFE Private Placement for Gross Proceeds of C$17 Million
Eloro Resources Ltd. (TSX: ELO) (FSE: P2QM) is pleased to announce the closing of its previously an... READ MORE
Minera Alamos Updates Resources and Reserves for the Pan Gold Mine in Nevada
Minera Alamos Inc. (TSX-V: MAI) (OTCQX: MAIFF) is pleased to announce updated Mineral Resource and M... READ MORE
Ero Copper Reports Fourth Quarter and Full Year 2025 Operating and Financial Results
Ero Copper Corp. (TSX: ERO) (NYSE: ERO) is pleased to announce its operating and financial results f... READ MORE
Rare Element Resources Announces Results of Oversubscribed Rights Offering of Common Shares
Rare Element Resources Ltd. (OTCQB: REEMF) is pleased to report that its previously announced... READ MORE
TRX Gold Reports Record Q2 2026 Production and Company Update
TRX Gold Corporation (TSX: TRX) (NYSE American: TRX) is pleased to announce preliminary resu... READ MORE