Marimaca Drills Pampa Medina Sulphides – Intersects Exceptional 6m of 12.0% Cu within 26m of 4.1% Cu in dominantly Bornite in SMRD-13, 40m of 2.1% Cu in SMD-02

Marimaca Copper Corp. (TSX:MARI) (ASX:MC2) is pleased to announce significant, high grade, sediment-hosted copper sulphide and oxide intersections which materially extend the Pampa Medina deposit in all directions. Pampa Medina is located at low altitude approximately 28km east of the Company’s Marimaca Oxide Deposit in a flat “pampa” valley within the Atacama Desert (Figure 1). Drilling targeted extensions of the shallow oxide-chalcocite mineralization at Pampa Medina and intersected ultra high-grade, bornite-chalcopyrite, disseminated chalcopyrite and high-grade oxide mineralization, which is hosted in a regionally extensive system of interbedded sedimentary rocks hosting the Pampa Medina deposit.
Highlights
- Drilling confirms Pampa Medina is part of a significant, flat lying, sediment hosted (stratiform) manto system, unique in Chile, that appears more analogous to the Kupfershiefer or African sediment hosted Cu deposits
- Thick (>15m true thickness), ultra high grade (>5% CuT) zones identified more than 600m apart in the same lithological horizon between SMRD-13 and SMR-01
- High-grade (>1.0% CuT), sedimentary-hosted copper mineralization defined by diamond drilling across a 600m east-west x 1,000m north-south area, with further drilling intersections indicating potential extensions to 1.4km x 1.2km
- Ultra high-grade bornite and chalcopyrite manto zones east, immediately down-dip, of Pampa Medina Deposit
- Highest grades correspond to interbedded shales, sandstones, conglomerates and tuffs
- Complements previous ultra high-grade zone encountered in SMR-01
- Hole SMRD-13 (true widths estimated to be 95% of reported intersection):
- 6m of 12.0% Cu from 594m downhole within 26m of 4.1% Cu from 580m and a broader 100m of 1.3% Cu from 580m
- Hole SMD-02 (drilled on section in between SMD-12 and SMD-13)
- 40m of 2.1% Cu from 282m downhole within 132m of 1.0% Cu from 278m
- Hole SMD-01 (~600m north-west of SMD-13)
- 68m of 1.2% Cu including 20m of 2.3% Cu from 298m downhole (previously reported)
- 22m of 1.7% Cu from 602m downhole
- Hole SMRD-12 (600m west of SMD-13)
- 56m of 1.4% Cu from 566m downhole
- Hole SMR-01 (adjacent to SMD-01) (previously reported)
- 56m of 2.1% including 18m of 5.0% Cu from 296m downhole within a broader 102m of 1.2% from 250m
- Hole SMD-03
- 42m of 0.72% Cu from 226m
- Primary sedimentary manto confirmed to carry high-grade (>>1% Cu) over significant true thickness (>70m) and area (600m x 1,000m) as demonstrated in SMR-01, SMD-01, SMRD-12, SMRD-13, SMD-02 and SMD-03
- Sedimentary units are generally flat lying, with a gentle easterly dip, and gentle northerly plunge, and both uplifted and down-dropped in certain blocks via a series of north-south faults
- Similar to the MOD, Pampa Medina’s location is expected to drive significant infrastructure and permitting benefits:
- Proximity to other mines and associated infrastructure (Figure 1): 28km from the MOD, 64km from Sierra Gorda (South32/KGHM), 40km from Mantos Blancos (Capstone Copper), 77km from Spence (BHP), 54km from Antucoya (Antofagasta Minerals)
- Low altitude, flat “pampa” type surface provides sufficient space for future facilities and infrastructure
- Proximity to existing powerlines, water pipelines, major ports and regional populations
- No private land ownership, limited human impact (no nearby local or indigenous population), extremely arid location indicates low permitting risks (comparable or superior to the MOD) associated with potential development
- The Company has added a second diamond drill rig at Pampa Medina and has budgeted a 14-hole follow up program targeting extensions and delineation of the mineralized manto (Figure 2)
- The previously announced Preliminary Economic Assessment (“PEA”) for Pampa Medina will be paused as the Company assesses what these drilling results may mean for the scale and development strategy of Pampa Medina
- Definitive Feasibility Study (DFS) for the MOD is near-complete, undergoing final review and will be released to the market in the near-term
Sergio Rivera, VP Exploration of Marimaca Copper, commented:
“Pampa Medina appears to be a Tier 1 prospect. Our exploration model, which is unconventional in Chile, has been proven correct. Firstly, the sedimentary units, which host Pampa Medina, are extensive and mineralized over many square kilometers and, secondly, the potential is confirmed for significant, very high grade, sulphide mineralization in these units.
This is the first time in my 40-year career that I have seen stratiform, sediment hosted, ultra high-grade copper in Chile of this potential scale. The intensity of bornite and chalcopyrite mineralization is truly remarkable. Between holes SMR-01, SMD-01, SMD-12, SMD-02, and now SMRD-13, we have defined an area of over 1,000m x 600m where we see continuity of the high-grade mineralization, well above 1% CuT, with some exceptionally high-grade areas as seen in SMRD-13 and SMR-01.
We are completing 10,000m of drilling across 14 diamond holes in the next phase. Our objective is to try to define the limits of the prospective sedimentary units, to understand the full potential of the Pampa Medina opportunity. We look forward to updating the market as we progress exploration on this exciting discovery.”
Hayden Locke, President & CEO of Marimaca Copper, commented:
“These results add a new dimension to our strategy and, we believe, strengthens our potential to be a globally significant copper producer intime. Our assessment is that the Pampa Medina and Madrugador oxide deposits already give us the potential to expand our copper cathode production profile and extend our mine life meaningfully from the nominal rates we are contemplating in the MOD DFS. With these thick, high-grade, sulphide intersections we now see the potential for a much larger scale copper system. Importantly, the location of Pampa Medina means it benefits from the same characteristics as our flagship MOD, such as access to first class infrastructure, proximity to workforces, lower permitting risk, and therefore any new discovery brought into development should be extremely competitive on a capital intensity basis.
Our primary objective remains to bring the MOD into production as quickly as is feasible and, in this respect, our DFS is largely complete and undergoing final peer reviews in preparation for release. Additionally, our permitting is progressing well with encouraging interactions across all of our stakeholder groups in Chile.
“Our exploration portfolio is vast and virtually untested. This extensional discovery highlights the ongoing opportunity for copper discoveries on a district scale. Our strategy remains two-fold: we will continue to advance the exciting exploration potential, both at Pampa Medina and other targets, whilst also transitioning, in the near-term, into a copper cathode producer.”
Overview of Pampa Medina
Pampa Medina is a manto-style copper deposit dominantly hosted in Jurassic-Triassic sedimentary units (sandstones, conglomerates, tuffs and black shales) overlain by andesitic volcanics and underlain by a Upper Paleozoic complex of metasediments and intrusions. Copper was originally identified in near-surface oxide mineralization dominated by atacamite, chrysocolla and both secondary and primary chalcocite, and has now been identified in high-grade zones of chalcopyrite and bornite which extend laterally down-dip beyond the oxide-primary transition.
Following Marimaca’s consolidation of the project area and surrounding land packages in 2024, the Company reinterpreted all available geological information (for the first time as one) and developed an updated geological model for Pampa Medina, which identified the lower sedimentary units of interbedded sandstones, shales and conglomerates as the productive horizons for future drill targeting. Oxide copper mineralization was logged in historical drilling in near-surface, uplifted blocks, with the model of continuity in the intact lithological sequence in deeper blocks for primary mineralization to be tested by Marimaca’s 2025 drilling campaign.
Hole SMRD-13 was collared 300m east from hole SMD-02, and 600m east on section from hole SMRD-12 to a total drilled depth of 800m (Figure 2). The hole intercepted the volcanic-sedimentary contact at 248m, where a lower-grade upper chalcopyrite manto was observed from 392m to 428m hosted by the tuff unit. Lower grade chalcopyrite mineralization was observed in the underlying shales and lesser sandstones up to 516m where a post-mineral diorite dyke intrudes the sediments. Beneath this, the main bornite-rich manto was intercepted from 580 to 606m. Mineralization transitioned form chalcopyrite>bornite into semi-massive bornite with fracture-fill and replacement textures. Highest-grade mineralization corresponded to a unit of heavily altered black shales stratabound between two sandstone units. Beneath this, weakly mineralized chalcopyrite and pyrite mineralized conglomerates and black shales were mapped to the bottom of hole (Figure 3).
Hole SMD-01 was drilled approximately 400m north of the northern margin of the known deposit at Pampa Medina. SMD01 was collared at Azimuth 270°, Dip -60° and drilled to a total depth of 950m (Figures 2 and 4). The collar was located 12m SE from SMR-01 but further deviated, reaching approximately 70m at the 650m depth. High grade copper oxide mineralization was intersected from 252m-494m downhole depth in an upper unit of sandstones and shales. Rhyolitic tuff, intruded by late dykes was intersected below the upper sediments from 492m to 564m and below that another more clastic rich unit extends up to the bottom of the hole. Metasediment basement was not reached at depth in hole SMD-01, meaning that the productive sedimentary unit increases in thickness towards the north. Mineralization transitioned to primary chalcopyrite and bornite mineralization at 550m. SMD-01 confirms the sediment-hosted oxide mineralization encountered in SMR-01, which is largely interpreted as the extension of the sediment-hosted manto deposits of Pampa Medina main. Historical drilling at Pampa Medina was generally limited to a depth of 400m, potentially too shallow to intersect the chalcopyrite-bornite dominant manto mineralization found in SMR-01, SMD-01 and now SMRD-13.
Holes SMD-02 and SMRD-12 and SMRD-13, were drilled at 300m spacings along an EW section N7440800, located 600m south from the SMR-01 & SMD-01 section (Figures 2, 3 and 4). The holes were designed to test the extension of the upper oxidized manto and the potential for a lower sulphide manto, as encountered in SMD-01. SMRD-02 intercepted mineralized sediments from 242m, consisting of shales and minor interbedded sandstones. The upper oxidized manto was intercepted from 282 to 324m. At depth, two consecutive mineralized mantos were encountered from 348m to 366m, with mixed mineralization, hosted in tuffs and from 376m to 410m of primary mineralization hosted by sandstones.
SMRD-12 intercepted weakly mineralized sandstones from 414m, increasing in intensity until the main chalcocite-bornite mineralized manto was intercepted from 566 to 620m hosted by lower sandstone units (Figure 4). At depth, a late diorite dyke intruded the sediments carrying trace pyrite and chalcopyrite. Hole SMD-03 was designed to test the continuity of the mineralization through a NW trending dyke corridor. The upper manto was intercepted with oxide mineralization from 226m to 268m, hosted by sandstones. The hole confirmed the previously interpreted WNW orientation of most of the post-mineral dykes.
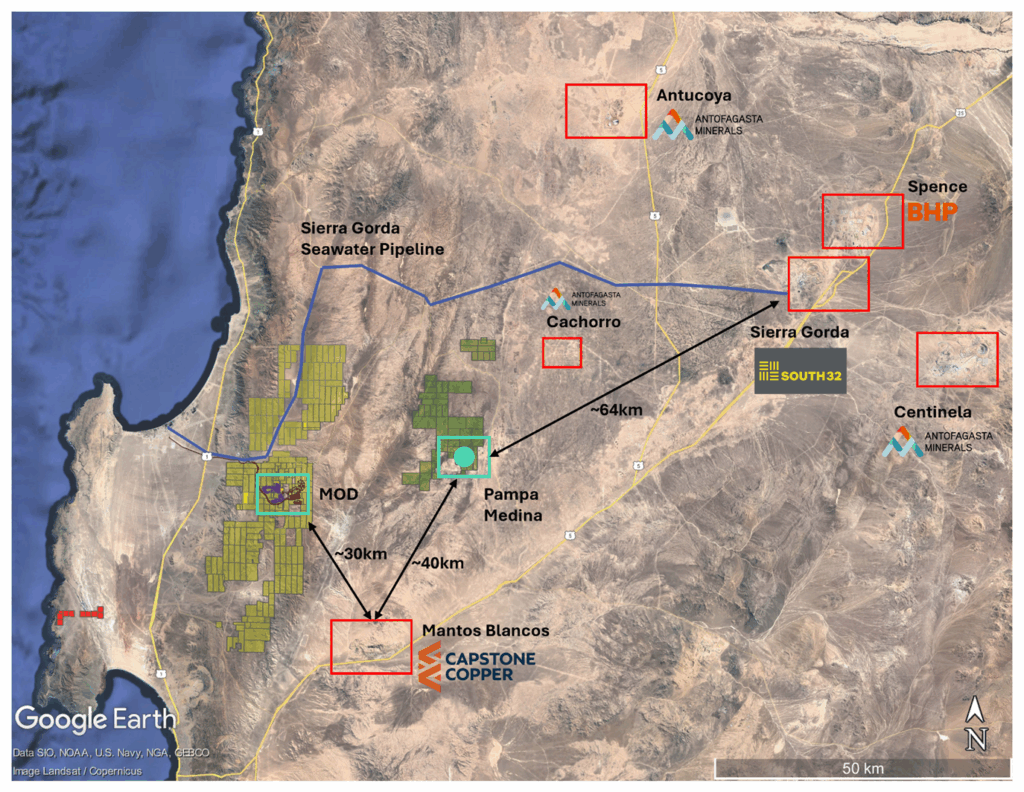
Figure 1: Regional Map – Marimaca, Pampa Medina and Regional Infrastructure
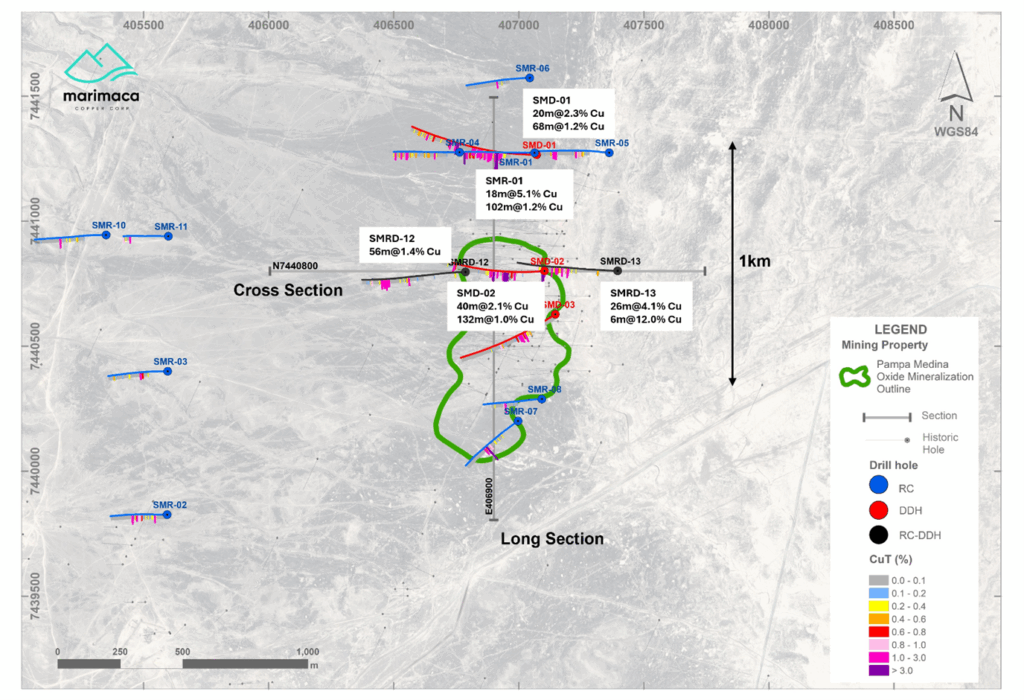
Figure 2 – Pampa Medina Deposit and Step-out Drilling Locations
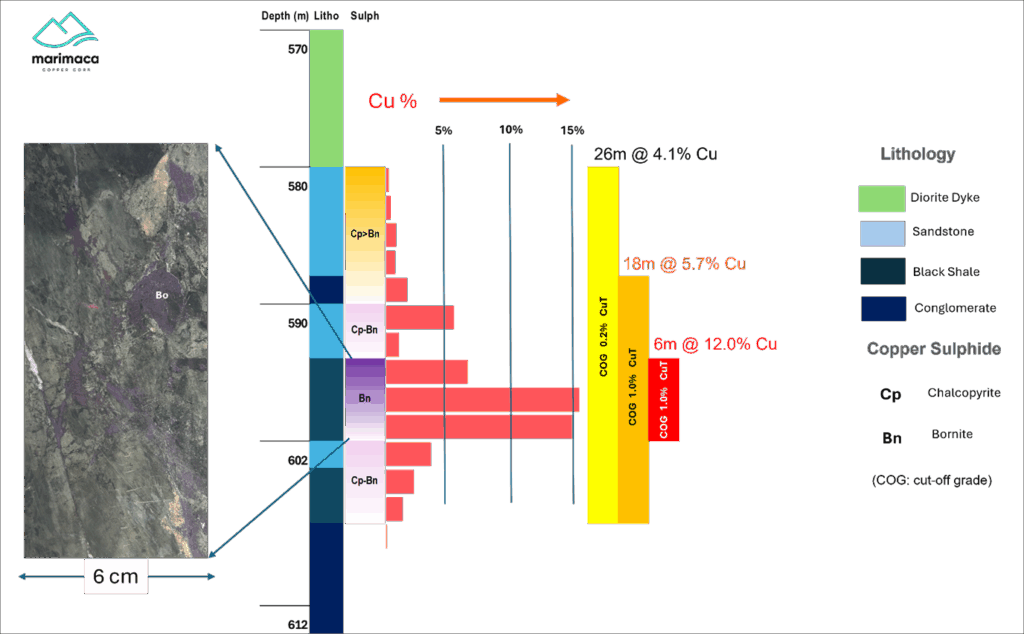
Figure 3 – Pampa Medina Lithology – SMRD-13 Downhole Sequence
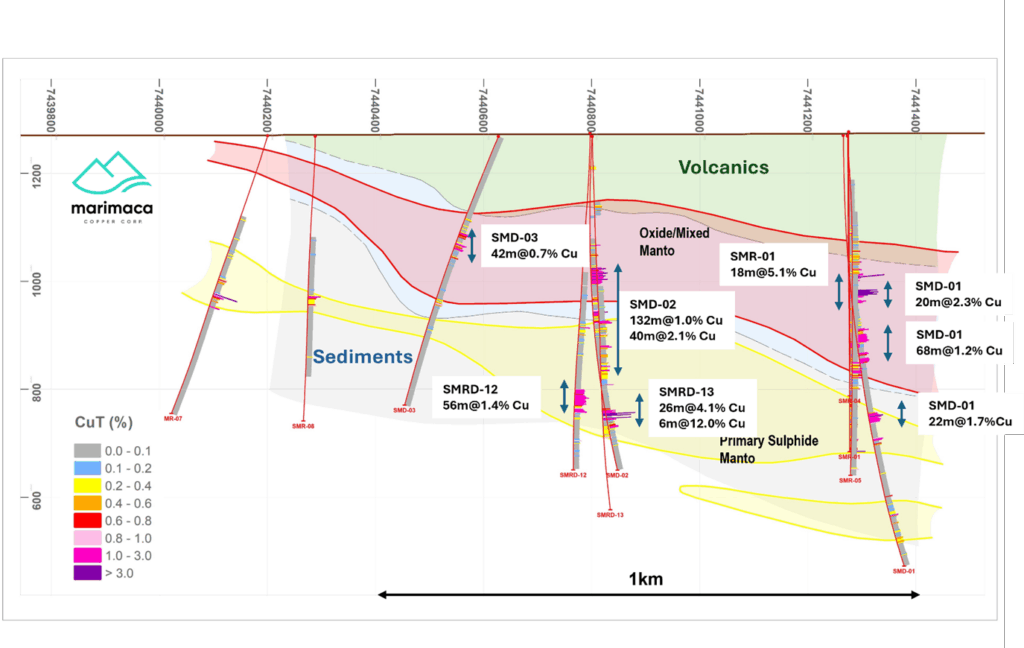
Figure 4 – Long Section Looking West – Pampa Medina
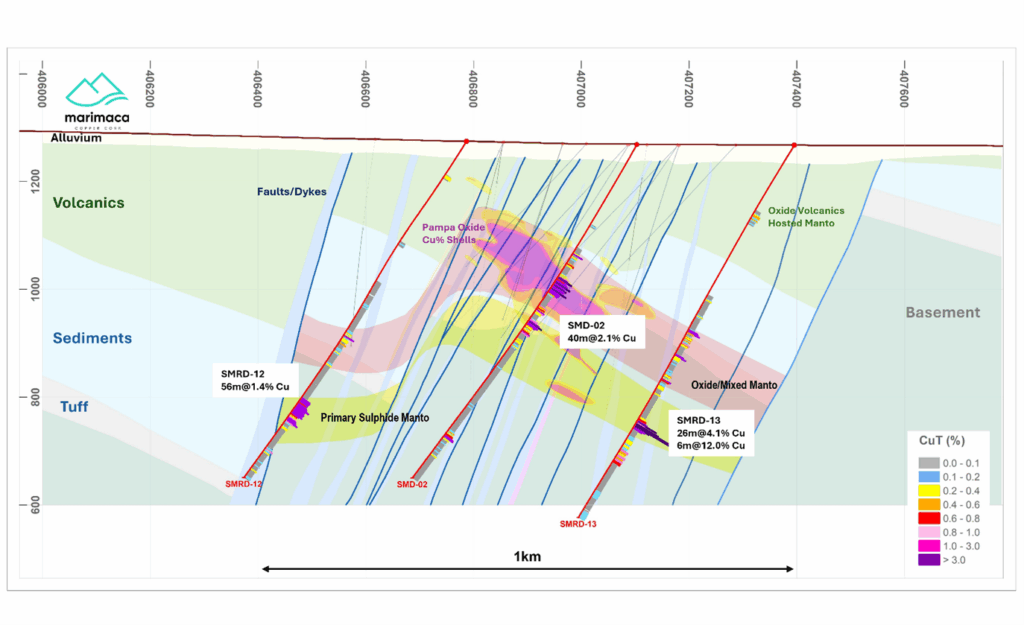
Figure 5 – Cross Section Looking North – Pampa Medina SMRD-12 to SMRD-13
| Hole | Total Depth (m) | From (m) | To (m) | Intersection (m) | % CuT | |
| SMD-01 | 952 | 252 | 494 | 242 | 0.65 | |
| Including | 298 | 366 | 68 | 1.20 | ||
| Including | 298 | 318 | 20 | 2.25 | ||
| And | 332 | 364 | 32 | 1.03 | ||
| And | 420 | 494 | 74 | 0.84 | ||
| Including | 420 | 460 | 40 | 1.07 | ||
| Including | 420 | 452 | 32 | 1.32 | ||
| And | 472 | 494 | 22 | 0.84 | ||
| 604 | 626 | 22 | 1.70 | |||
| SMD-02 | 750 | 278 | 410 | 132 | 0.99 | |
| Including | 282 | 322 | 40 | 2.06 | ||
| SMD-03 | 650 | 226 | 268 | 42 | 0.72 | |
| SMRD-12 | 750 | 566 | 622 | 56 | 1.37 | |
| Including | 582 | 590 | 8 | 2.00 | ||
| SMRD-13 | 800 | 580 | 680 | 100 | 1.28 | |
| Including | 580 | 648 | 68 | 1.65 | ||
| Including | 580 | 606 | 26 | 4.07 | ||
| Including | 594 | 600 | 6 | 11.98 |
Table 1: Table of Intersections
| Hole | Easting | Northing | Elevation | Azimuth | Inclination | Depth |
| SMD-01 | 407071.42 | 7441265.92 | 1270.04 | 270 | -60 | 950 |
| SMD-02 | 407103.09 | 7440800.85 | 1268.64 | 270 | -60 | 750 |
| SMD-03 | 407146.04 | 7440627.56 | 1268.32 | 240 | -50 | 650 |
| SMRD-12 | 406786.97 | 7440797.22 | 1274.92 | 270 | -60 | 750 |
| SMRD-13 | 407395.34 | 7440801.29 | 1267.63 | 270 | -60 | 800 |
Table 2: Drill Collars
Sampling and Assay Protocols
True widths are estimated as 95% of reported intervals, based on down-hole bedding and structural measurements. DDH holes were sampled on a 2m continuous basis, halved by a conventional core splitter on site with one half sent to the Andes Analytical Assay preparation laboratory in Copiapó and the pulps then sent to the same company laboratory in Santiago for assaying. Samples were prepared using the following standard protocol: drying; crushing all sample to -1/4” and passing through a secondary crusher to better than 80% passing -10#; homogenizing; splitting; pulverizing a 400-600g subsample to 95% passing -150#; and a 125g split of this sent for assaying. All samples were assayed for %CuT (total copper); %CuS (acid soluble copper). A full QA/QC program, involving insertion of appropriate blanks, standards and duplicates was employed with acceptable results. Pulps and sample rejects are stored by Marimaca Copper for future reference.
Qualified Person / Competent Person
The technical information in this news release, including the information that relates to geology, drilling and mineralization was prepared under the supervision of, or has been reviewed by Sergio Rivera, Vice President of Exploration, Marimaca Copper Corp, a geologist with more than 40 years of experience and a member of the Colegio de Geólogos de Chile and of the Institute of Mining Engineers of Chile, and who is the Qualified Person for the purposes of NI 43-101 responsible for the design and execution of the drilling program.
The information in this announcement which relates to exploration results for the Pampa Medina Project is based on, and fairly reflects, information and supporting documentation prepared by Sergio Rivera, VP Exploration of Marimaca, a Competent Person who is a member of the Comision Minera (Chilean Mining Commission), Colegio de Geólogos de Chile and of the Institute of Mining Engineers of Chile. Mr. Rivera has sufficient experience that is relevant to the style of mineralisation and types of deposit under consideration and to the activity being undertaken to qualify as a Competent Person as defined in the 2012 Edition of the Joint Ore Reserves Committee Australasian Code for Reporting of Exploration Results, Mineral Resources and Ore Reserves. Mr. Rivera consents to the inclusion in this announcement of the matters based on his information in the form and context in which it appears.
MORE or "UNCATEGORIZED"
First Phosphate Receives Conditional Approval for up to $16.7 Million Non-Repayable Contribution from the Government of Canada
First Phosphate Corp. (CSE: PHOS) (OTCQX: FRSPF) (OTCQX ADR: FPHOY) (FSE: KD0) has been cond... READ MORE
Gold X2 Drills 117m of 1.21 g/t Au, Including 10m of 4.37g/t Au; High-Grade Zone Intersected 280m Beneath the Resource Pit Demonstrating Underground Potential at the Moss Gold Deposit
Gold X2 Mining Inc. (TSX-V: AUXX) (OTCQB: GSHRF) (FWB: DF8), is pleased to announce initial drilling... READ MORE
Tectonic Raises Over C$92 Million; Completes Upsized Private Placement With Full Over-Allotment Exercised
Tectonic Metals Inc. (TSX-V: TECT) is pleased to announce the successful closing of the Company’s ... READ MORE
Cerro de Pasco Resources Enters Project Development Funding Agreement with U.S. International Development Finance Corporation for Quiulacocha
Cerro de Pasco Resources Inc. (TSX-V: CDPR) (OTCQB: GPPRF) (BVL: CDPR) announces that it has ... READ MORE
NorthWest Announces Updated Mineral Resource at Kwanika Reflecting Strategic Shift to Higher-Grade Copper-Gold Focus
NorthWest Copper Corp. (TSX-V: NWST) is pleased to announce an updated mineral resource estimate for... READ MORE