Copper Mountain Intersects Highest Grade Copper-Gold Mineralization including 104 metres of 1.01% CuEq and Extends Mineralized Zone Over 200 Metres at Depth
Copper Mountain Mining Corporation (TSX: CMMC) (ASX: C6C) is pleased to announce positive results from the first four drill holes of its 2023 exploration program at the Copper Mountain Mine, located in southern British Columbia. Two of these holes were drilled at the Copper Mountain Mine main pit and two at New Ingerbelle, which is located approximately one kilometre to the west of the main pit.
Drill hole CM-DD-897 intersected the highest-grade and most gold-rich, copper-gold mineralization yet discovered at New Ingerbelle and extends the known mineralized zone by approximately 200 metres below the current Mineral Resource. This drill hole shows that the mineralized zone at New Ingerbelle has a vertical extent of at least 900 metres and the zone remains open both laterally and at depth.
Drilling Highlights
- Drill hole CM-DD-897
- 191 metres of 0.66% CuEq (0.45% Cu, 0.32 g/t Au, 0.41 g/t Ag) from 722 metres
- Including 104 metres of 1.01% CuEq (0.65% Cu, 0.52 g/t Au, 0.53 g/t Ag) from 809 metres
- Including 45 metres of 1.50% CuEq (0.94% Cu, 0.83 g/t Au, 0.74 g/t Ag) from 867 metres
- Drill hole CM-DD-896
- 108 metres of 0.76% CuEq (0.59% Cu, 0.23 g/t Au, 2.13 g/t Ag) from 464 metres
- Including 56 metres of 1.00% CuEq (0.79% Cu, 0.27 g/t Au, 3.59 g/t Ag) from 466 metres
- Drill hole CM-DD-895
- 42 metres of 0.74% CuEq (0.64% Cu, 0.13 g/t Au, 1.47 g/t Ag) from 480 metres
“Our current drill program has discovered high-grade copper-gold mineralization over 200 metres below the previous deepest drill hole at New Ingerbelle and shows that the mineralizing system becomes stronger and more gold-rich at depth,” commented Patrick Redmond, Copper Mountain’s Senior Vice President, Exploration and Geoscience. “We have been successful in achieving the objective of our 2023 exploration program, which is designed to look for higher-grade zones below and adjacent to the current resource. What we have found is similar to the high-grade zones at Red Chris and Cadia-Ridgeway. These latest drilling results continue to demonstrate the size potential of the Copper Mountain Mine.”
2023 Exploration Program
The 2023 exploration program is designed to test seven target areas within the NW-trending Copper Mountain-New Ingerbelle mineralized corridor (Figure 1), a 4 to 5 kilometre long, NW-trending zone of porphyry copper-gold mineralization. Multiple historical drill holes within this zone end in copper-gold mineralization and geophysical data strongly suggest that the mineralizing system extends well below the current known Mineral Resource, which is open both laterally and at depth.
Figure 1 provides the location map showing the 2023 target areas numbered 1 to 7, the historical Titan IP chargeability data (7 lines completed in 2007), the 2023 geophysical survey grid, and all drill holes colour-coded by copper grade. The 2023 survey comprises a 3D IP/DC resistivity survey at New Ingerbelle and to the northwest of the active mining area, plus a series of 2D IP/DC resistivity lines within and to the east of the active mining area.
The 2023 drill program consists of two phases. Phase 1 is expected to be completed mid-year and includes a large geophysical program and approximately 8,000 metres of diamond drilling. Phase 2 consists of approximately 10,000 metres of additional drilling. At New Ingerbelle, drilling is currently ongoing with three holes completed and one hole in progress. At the Copper Mountain Mine, two holes have been completed and one hole is in progress, which is a 175-metre undercut of a 2010 drill hole that intersected a 72-metre zone grading 1.86% CuEq from 452 metres at depth (Target area 5 on Figure 1).
The current drill program is focused on finding higher-grade zones of mineralization below and adjacent to the current Mineral Resource, and similar to the higher-grade zones that have been discovered at other alkalic porphyry copper-gold deposits such as Red Chris in British Columbia and Cadia-Ridgeway in New South Wales, Australia. The Copper Mountain deposit is the same geological age as the Red Chris deposit and both contain the same style of high-grade, A-quartz vein-hosted, copper-gold mineralization hosted within potassically-altered porphyry intrusions and adjacent country rock. Like Red Chris, copper and gold at the Copper Mountain deposit exhibit a strong correlation and Au/Cu ratios increase inward towards the core of the system. The discovery in hole CM-DD-897 of high-grade copper-gold mineralization, with Au/Cu ratios of >1 in the highest-grade interval, shows that the mineralizing system at New Ingerbelle becomes stronger and more gold-rich at depth. The mineralized zone has a minimum vertical extent of 900 metres and remains open at depth. For comparison, zones of high-grade mineralization at Red Chris and Cadia-Ridgeway exhibit vertical extents of over 1,000 metres. Figure 2 shows New Ingerbelle and the East Ridge zone at Red Chris at the same scale.
The Red Chris cross section is taken from “Newcrest Mining Limited – Exploration Update 10 March 2021” and shows the location of the East Ridge discovery hole, RC678. The newly discovered higher-grade copper-gold zone at New Ingerbelle has similar grades to Red Chris, and the Company believes the overall mineralizing system is comparable in size.
A large geophysical program is also ongoing and is designed to infill and extend previous induced polarization/DC resistivity coverage. A 3D survey has been completed at New Ingerbelle and both 3D and 2D surveys have been completed at the Copper Mountain Mine. A magnetotellurics survey is currently ongoing at New Ingerbelle and will extend the depth of investigation below the limits of the IP/DC resistivity survey. Large numbers of physical property measurements on drill core, including density, magnetic susceptibility, resistivity and chargeability have also been carried out on recent and historical drill core and will be used to constrain the geophysical modelling. These new geophysical and petrophysical data will be integrated with historical geophysical data and will be used to better define existing targets and to generate new target areas.
Drilling Results
A list of the drill holes including significant intercepts and other details are included in Appendix A. Location maps and cross sections of the four holes are shown in Appendix B. Drilling to date has tested three of the target areas shown in Figure 1 with drilling currently ongoing on a fourth target area. The strategy for Phase 1 of the program is to drill into multiple target areas and then, based on the results, prioritize target areas for follow-up drilling in Phase 2.
Drill Holes CM-DD-894 and CM-DD-895
Drill holes CM-DD-894 and CM-DD-895 (Target area 4 on Figure 1) were drilled 160 metres apart to test a strong IP chargeability feature (on the most westerly line from the 2007 IP/DC resistivity survey) located immediately north of the Copper Mountain Stock (“CMS”) and on trend to the northwest from the current mining area in the Copper Mountain main pit shown in Figure 1. Appendix B, Figure 3 shows a location map and Figure 4 shows a cross section with drill holes CM-DD-894 and CM-DD-895. The highest-grade intervals occur within zones of porphyry-related hydrothermal breccia, including a 42-metre zone grading 0.74% CuEq from 480 metres depth in hole CM-DD-895.
Most of the previous drilling in this area has consisted of relatively short holes. A drill hole from 2008 (08P1-22), located approximately 200 metres to the west of the current drilling, intersected a 46-metre zone grading 0.65% CuEq from 374 metres at depth. Reconnaissance mapping of the area in 2022 identified a large, approximately 300 x 300 metre, zone with porphyry-style veins and related potassic alteration and anomalous copper values. Mapping also located two historical adits in the area. Grab samples from waste piles outside these adits returned values greater than 1% Cu in rocks with A-quartz veins, chalcopyrite veinlets and Kspar-biotite-magnetite alteration.
Both holes intersected copper-gold mineralization below the current Mineral Resource, and further drilling in the area is warranted. This area of the deposit is the location of the future haul road to New Ingerbelle and a deeper reserve pit would have a positive impact on road construction costs and haul distances.
Drill Hole CM-DD-896
Drill hole CM-DD-896 (Target area 1 on Figure 1) was a 200-metre undercut of high-grade porphyry-hosted copper-gold mineralization in a number of 2021 drill holes, including drill hole 21IG-11 located in the southwest area of New Ingerbelle (See Appendix B, Figure 5 and 6). Drill hole CM-DD-896 intersected a wide zone of chalcopyrite-pyrite mineralization hosted in Nicola Group rocks, Lost Horse porphyry dykes and related hydrothermal breccias. The highest-grade interval of 56 metres at 1.00% CuEq is mainly hosted in a biotite-sulfide cemented hydrothermal breccia. The mineralization intersected in this drill hole is below the current Mineral Resource, and the mineralized zone remains open to the southwest towards the CMS contact.
Drill Hole CM-DD-897
Drill hole CM-DD-897 (Target area 2 on Figure 1) was a 200-metre undercut of the previous deepest drill hole at New Ingerbelle, 20IG01, which intersected a number of intervals of high-grade copper-gold mineralization (See Appendix B, Figure 7). Mineralization in CM-DD-897 is hosted within igneous breccias and Nicola Group country rocks and consists of a chalcopyrite-pyrite sulphide assemblage associated with potassic alteration (hydrothermal quartz-magnetite, biotite and potassium feldspar), with local pyrrhotite associated with specific lithological units within the Nicola Group. The interval is also cut by narrow Lost Horse porphyry dykes, with quartz-chalcopyrite veins, chalcopyrite-pyrite veinlets, and locally intense potassic alteration. The highest-grade interval, 8.85 metres at 5.37% CuEq, consists of a quartz-magnetite-chalcopyrite-pyrite assemblage, hosted in what appears to be intensely altered Nicola Group rocks.
QA/QC and Core Sampling Protocols
Drill core was cut and sampled at the Copper Mountain Mine core processing facility. Half core samples were collected in plastic bags together with sample tags and grouped in “apple crates” for dispatch to the assay laboratory. Sample size is approximately 2 metres for HQ and 3 metres for NQ core diameters but may vary to honour geological contacts. Sample weights typically varied from 5 to 10 kilograms. Sample sizes are considered appropriate for the style of mineralization. Drill core samples were transported by road to the laboratory. Sample preparation and assay analysis was conducted at the independent ISO 9001 certified and ISO 17025 accredited MSALABS in Langley, British Colombia. All samples were dried, crushed to 70% passing 2 mm, with a 250-gram split pulverized to 85% passing 75µm. All samples were assayed for 48 elements using a 4-acid digestion followed by ICP-AES/MS determination (method IMS-230). Overlimit (>10,000 ppm) copper was determined using ICP-AES (method ICF-6Cu). Gold analyses were determined by 30-gram fire assay with an AAS finish (method FAS-111). Sampling and assaying quality control procedures consisted of inclusion of certified reference material (“CRMs”), blank material and duplicates with each batch (at least 1:20). Assays of quality control samples were compared with reference samples in Excel and verified as acceptable prior to use of data from analyzed batches. Laboratory quality control data, including laboratory standards, blanks, duplicates, repeats and grind size results are captured in an Excel database and assessed for accuracy and precision for recent data. Analysis of the available quality control sample assay results indicates that an acceptable level of accuracy and precision has been achieved. Sampling, sample preparation and quality control protocols are considered appropriate for the material being sampled. There are no known issues that would materially affect the accuracy or reliability of the analytical data from the drill program presented herein.
Competent Persons Statement
The information in this report that relates to exploration targets, exploration results, Mineral Resources or ore reserves is based on information compiled by Patrick Redmond, Ph.D., P. Geo. Patrick Redmond is a full-time employee of the Company and has sufficient experience which is relevant to the style of mineralization and type of deposit under consideration and to the activity being undertaken to qualify as a Competent Person as defined in the 2012 Edition of the ‘Australasian Code for Reporting of Exploration Results, Mineral Resources and Ore Reserves’. Patrick Redmond consents to the inclusion in this news release of the matters based on the information in the form and context in which it appears.
Qualified Person
Patrick Redmond is a qualified person as defined by National Instrument 43-101 – Standards of Disclosure for Mineral Projects and has reviewed and approved the technical content of this release.
About Copper Mountain Mining Corporation
Copper Mountain owns 75% of the Copper Mountain Mine, which is located in southern British Columbia near the town of Princeton. The Copper Mountain Mine produces approximately 100 million pounds of copper equivalent on average per year.
APPENDIX A: Drill Hole Data
Table 1: Drill Hole Details
| Hole ID | Easting (m) | Northing (m) | Elevation (m) | Azimuth (°) | Dip (°) | Total Depth (m) |
| CM-DD-894 | 678804 | 5467470 | 1062 | 180 | -55.00 | 605 |
| CM-DD-895 | 678802 | 5467615 | 1062 | 170 | -63.00 | 773 |
| CM-DD-896 | 677307 | 5467632 | 1136 | 310 | -65.00 | 1064 |
| CM-DD-897 | 678070 | 5468110 | 875 | 255 | -60.00 | 1090 |
Table 2: Significant Intercept Table(1,2,3)
| Hole ID | From (m) | To (m) | Length (m) | CuEq% | Cu% | Au g/t | Ag g/t |
| CM-DD-894 | 59.08 | 95.08 | 36.00 | 0.61 | 0.46 | 0.21 | 0.93 |
| including | 68.83 | 87.34 | 18.51 | 1.04 | 0.79 | 0.35 | 1.62 |
| 107.18 | 126.00 | 18.82 | 0.22 | 0.17 | 0.07 | 0.32 | |
| 297.39 | 314.14 | 16.75 | 1.91 | 1.65 | 0.35 | 3.02 | |
| CM-DD-895 | 137.10 | 153.45 | 16.35 | 0.60 | 0.50 | 0.13 | 1.19 |
| 479.54 | 521.13 | 41.59 | 0.74 | 0.64 | 0.13 | 1.47 | |
| CM-DD-896 | 464.20 | 572.47 | 108.27 | 0.76 | 0.59 | 0.23 | 2.13 |
| including | 465.56 | 521.50 | 55.94 | 1.00 | 0.79 | 0.27 | 3.59 |
| 597.00 | 619.85 | 22.85 | 0.28 | 0.21 | 0.10 | 0.32 | |
| 690.75 | 713.00 | 22.25 | 0.45 | 0.35 | 0.14 | 0.51 | |
| CM-DD-897 | 24.00 | 88.70 | 64.70 | 0.47 | 0.31 | 0.23 | 0.79 |
| Assays Pending | |||||||
| 208.62 | 242.00 | 33.38 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 0.11 | 0.34 | |
| 255.20 | 329.78 | 74.58 | 0.29 | 0.21 | 0.12 | 0.37 | |
| including | 257.10 | 278.57 | 21.47 | 0.62 | 0.42 | 0.28 | 0.71 |
| 352.30 | 419.20 | 66.90 | 0.28 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.28 | |
| 455.00 | 503.00 | 48.00 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 0.11 | 0.26 | |
| 616.70 | 648.08 | 31.38 | 0.42 | 0.33 | 0.13 | 0.38 | |
| 607.73 | 648.08 | 40.35 | 0.36 | 0.28 | 0.12 | 0.32 | |
| 674.00 | 698.18 | 24.18 | 0.23 | 0.16 | 0.10 | 0.28 | |
| 722.00 | 912.75 | 190.75 | 0.66 | 0.45 | 0.32 | 0.41 | |
| including | 808.90 | 912.75 | 103.85 | 1.01 | 0.65 | 0.52 | 0.53 |
| including | 867.50 | 912.75 | 45.25 | 1.50 | 0.94 | 0.83 | 0.74 |
| including | 903.90 | 912.75 | 8.85 | 5.37 | 3.12 | 3.33 | 2.20 |
| Notes: | |||||||
| 1. | Reporting Criteria: Intercepts reported are downhole drill width (not true width). CuEq >0.13%, minimum 15 metres downhole length, maximum internal waste dilution of 15 metres, and a maximum consecutive waste of 10 metres. Higher-grade included intervals are reported at CuEq >0.3%, >0.5% and >1.0%, with a minimum 5 metre downhole length for the >1.0% composites |
||||||
| 2. | Copper and gold grades are reported to 2 significant figures. Copper equivalent values (CuEq%) are calculated using metal prices of US$3.60, US$1,650, US$21.35 and for Cu, Au, and Ag, respectively, with no metal recovery factors applied. |
||||||
| 3. | Samples are from core drilling which is HQ or NQ in diameter. Core is photographed and logged by the Company’s geology team before being cut. Half core HQ and NQ samples are prepared for assay and the remaining material is retained at site for future reference. Each assay batch is submitted with duplicates, standards and blanks to monitor laboratory quality. Total depth (end of hole) is rounded to the nearest metre for reporting purposes. |
||||||
APPENDIX B: LOCATION MAPS AND CROSS SECTIONS
Figure 3 shows a plan map with the location of holes CM-DD-894 and CM-DD-895. Previous drill holes are colour-coded by grade. Most of the previous drilling in this area has consisted of relatively short holes (see Figure 4). Note the location of two historical adits. C-C’ shows the locations of the cross section shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4 shows a cross section with drill holes CM-DD-894 and CM-DD-895 plotted on a 2D IP chargeability data. Reserve pit and Whittle Resource Shell are based on Copper Mountain’s NI 43-101 technical report titled “Life-of-Mine Plan and 65 kt/d Expansion Study Update NI 43-101 Technical Report, Princeton, British Columbia” with an effective date of August 1, 2022 and dated September 30, 2022 (the “2022 Technical Report”).
Figure 5 shows the location of drill holes CM-DD-896 and CM-DD-897 as well as previous drill holes at New Ingerbelle, with the drill holes colour coded by grade. Lines A-A’ and B-B’ show locations of cross sections shown in Figures 6 and 7, respectively. The reserve pit is based on the 2022 Technical Report.
Figure 6 provides a cross section showing drill hole CM-DD-897 and the outline of high-grade copper-gold zone (>1.0% CuEq), shown by the dashed red line and red shading. Drill hole CM-DD-897 intersected the highest-grade and most gold-rich, copper-gold mineralization yet discovered at New Ingerbelle and shows that the mineralizing system is getting stronger at depth. Drill holes 20IG-01 and 21IG-38 noted in the figure were drilled in 2021 and previously reported by the Company. The location of the cross section is shown in Figure 5.
Figure 7 provides a cross section showing hole CM-DD-897 looking Northeast. The location of the cross section is shown in Figure 5
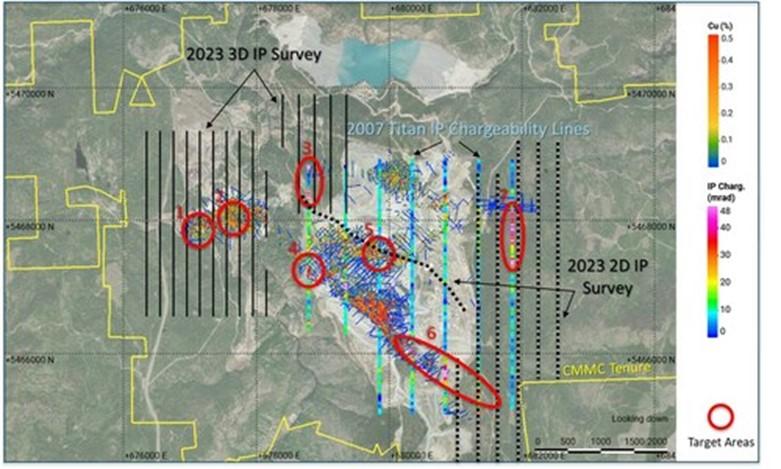
Figure 1: Drill program target areas (CNW Group/Copper Mountain Mining Corporation)
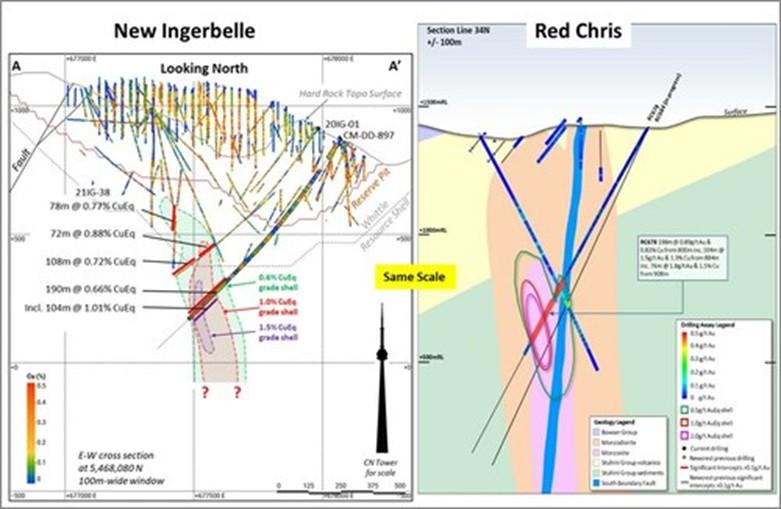
Figure 2: New Ingerbelle and Red Chris cross sections (CNW Group/Copper Mountain Mining Corporation)
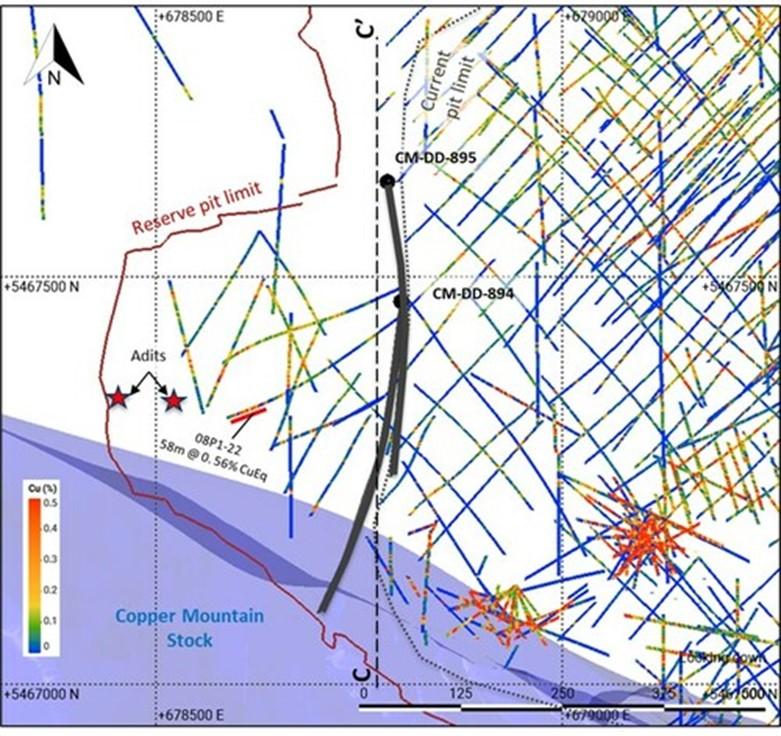
Figure 3 – Location Map for holes CM-DD-894 and CM-DD-895 (CNW Group/Copper Mountain Mining Corporation)
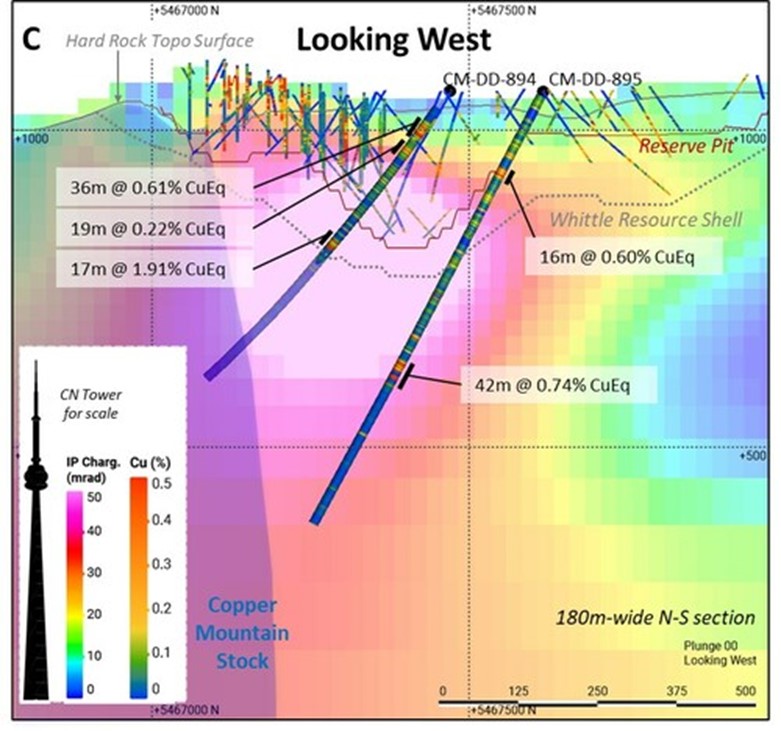
Figure 4: Drill Holes CM-DD-894 and CM-DD-895 (Cross Section) (CNW Group/Copper Mountain Mining Corporation)
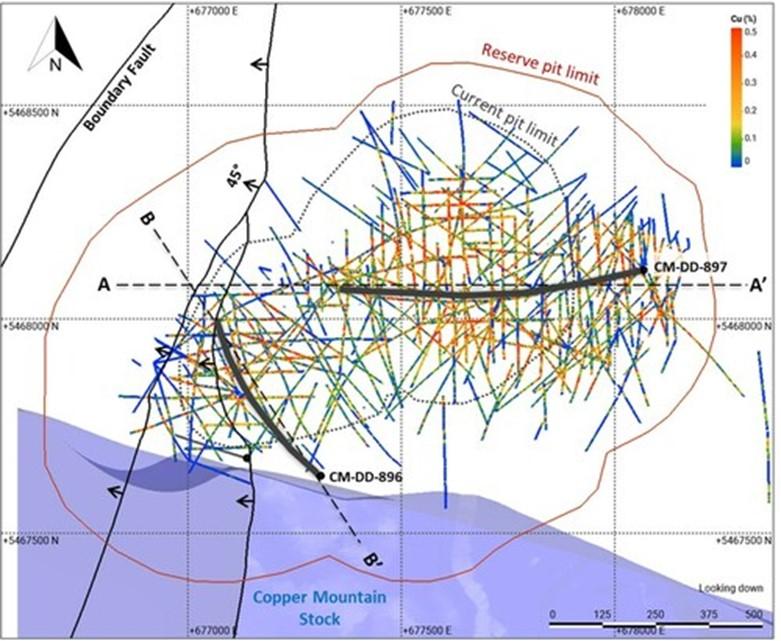
Figure 5: Drill holes CM-DD-896 and CM-DD-897 (Location Map) (CNW Group/Copper Mountain Mining Corporation)
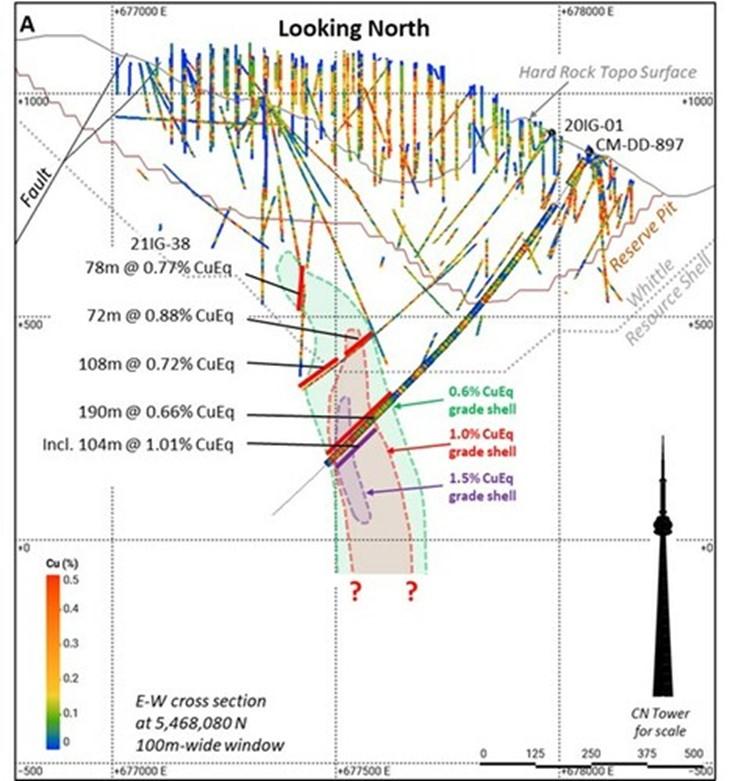
Figure 6: Drill hole CM-DD-897 (Cross Section) (CNW Group/Copper Mountain Mining Corporation)
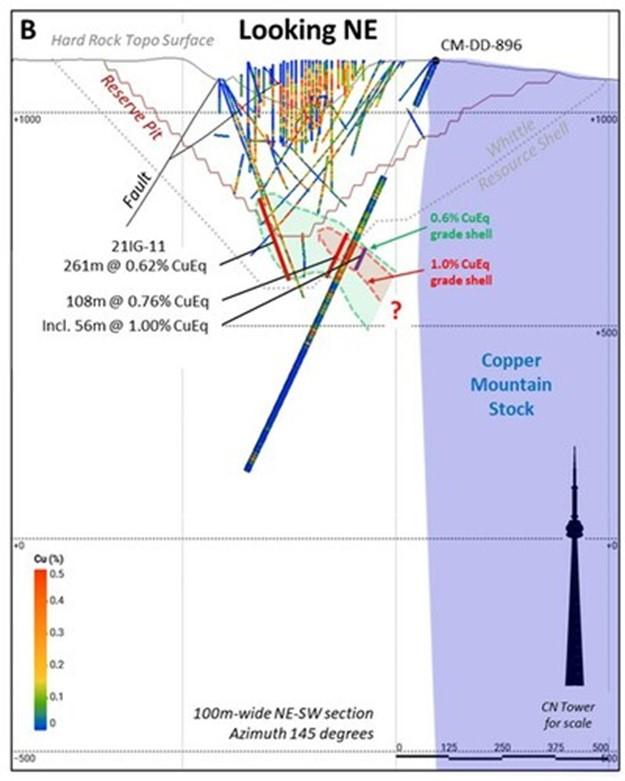
Figure 7: Drill hole CM-DD-897 (Cross Section) (CNW Group/Copper Mountain Mining Corporation)
MORE or "UNCATEGORIZED"
Minera’s Copper Subsidiary Acquires Suaqui Verde Copper Project in Sonora, Mexico
Minera Alamos Inc. (TSX-V:MAI) is pleased to announce the executi... READ MORE
SILVERCORP TO ACQUIRE ADVENTUS, CREATING A GEOGRAPHICALLY DIVERSIFIED MINING COMPANY BY ADDING THE ADVANCED EL DOMO PROJECT
Silvercorp Metals Inc. (TSX: SVM) (NYSE American: SVM) and Advent... READ MORE
Vortex Metals Announces Closing of Upsized Private Placement
Vortex Metals Inc. (TSXV: VMS) (FSE: DM8) (OTCQB: VMSSF) is plea... READ MORE
Gatos Silver Reports South-East Deeps Drilling Results at Cerro Los Gatos and Announces Executive Appointment
Gatos Silver, Inc. (NYSE:GATO) (TSX: GATO) provided an update on ... READ MORE
Eldorado Gold Reports First Quarter 2024 Financial and Operational Results; Steady Start to 2024
Eldorado Gold Corporation (TSX: ELD) (NYSE: EGO) reports the Comp... READ MORE